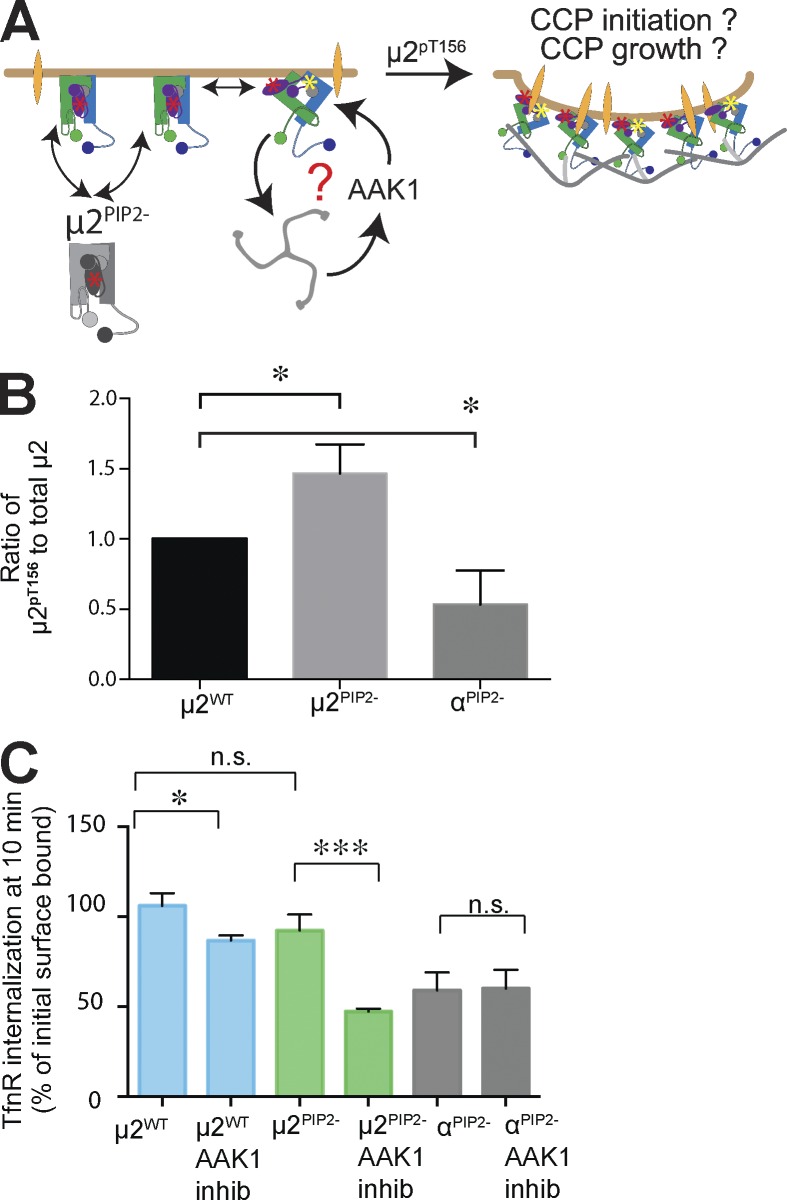
Figure 6.
Increased phosphorylation of µ2 at T156 compensates to maintain efficient TfnR internalization in µ2PIP2− cells. (A) Schematic representation of the potential roles for AAK1 activation and phosphorylation of T156 on µ2. The question mark and arrows point to possible compensatory mechanisms and a positive feed-forward loop that can restore efficient CME in µ2PIP2− cells. (B) Quantification (mean ± SD, n = 3; two-tailed Student’s t tests were used to assess statistical significance: *, P < 0.05) of total and phosphorylated µ2pT156 subunit in µ2WT, µ2PIP2-, and αPIP2− cells (see also Fig. S5 B). (C) TfnR uptake measured at 10 min in control, µ2PIP2−, and αPIP2− cells with or without treatment with the 10-µM AAK1 inhibitor (inhib), Compound 2. Data shown are mean ± SD, n = 3; normalized to total surface bound; *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.0005. n.s., not significant.