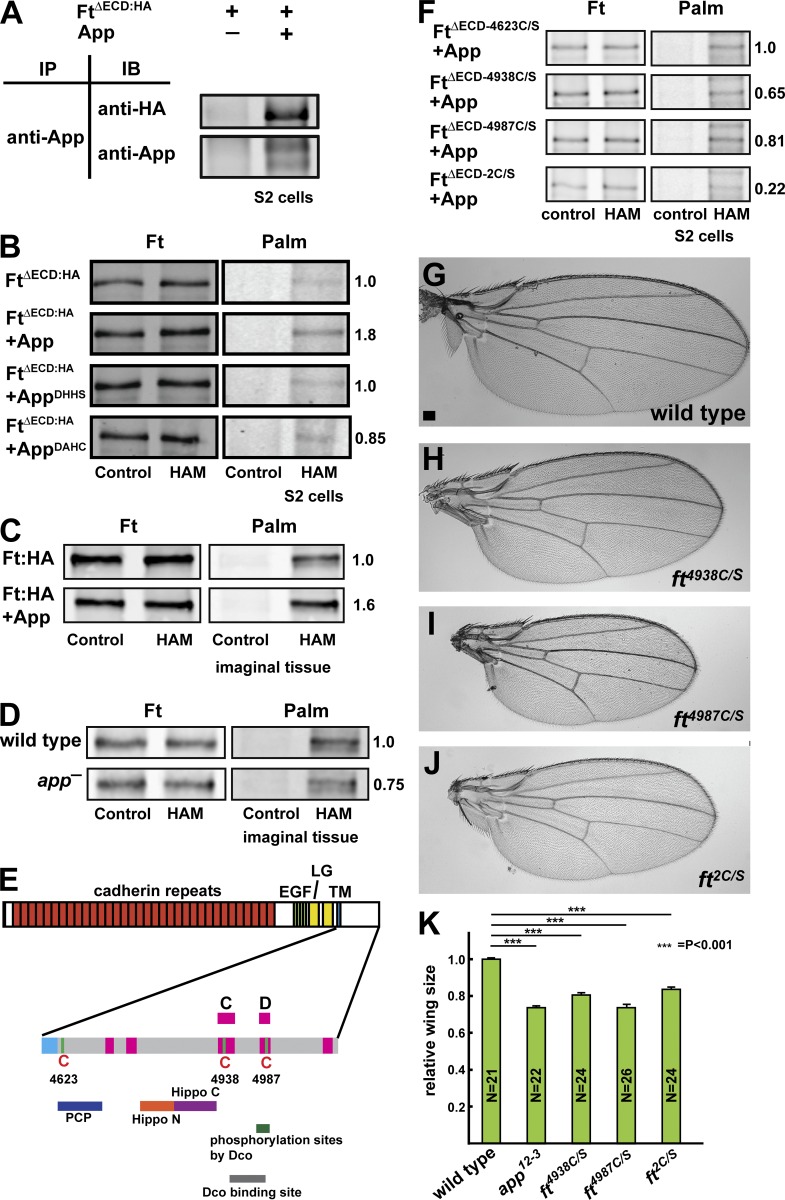
Figure 4.
Ft associates with and is palmitoylated by App. (A) Coimmunoprecipitation between App and FtΔECD in S2 cells. (B) App promotes palmitoylation of Ft in S2 cells. Mutation of the App DHHC motif (AppDHHS or AppDAHC) blocks this effect. Palm, palmitoylation. (C and D) Ft is palmitoylated by App in imaginal disc epithelia. Bands shown represent the 110-kD C-terminal fragment of Ft, which includes the ICD, treated with phosphatase. Immunoprecipitated Ft is palmitoylated, and coexpression of App promotes increased palmitoylation (C). Palmitoylation of 110-kD Ft is reduced in app12-3 mutant imaginal discs (D). (E) The cysteine residues and functional domains in Ft-ICD (adapted from Matakatsu and Blair, 2012; Pan et al., 2013). The regions conserved between Ft and its human orthologue FAT atypical Cadherin 4 are shown in pink, and known functional domains are shown underneath. Conserved cysteine residues at 4,623, 4,938, and 4,987 are indicated. EGF, EGF-like domain; LG, Laminin G domain; TM, transmembrane domain. (F) Mapping of Ft palmitoylation sites using S2 cells. Mutation of Cys4623 (FtΔECD-4623C/S) does not appear to affect Ft palmitoylation. Mutation of either Cys4938 (FtΔECD-4938C/S) or Cys4987 (FtΔECD-4987C/S) moderately decreases palmitoylation, whereas mutation of both together (FtΔECD-2C/S) more severely affects palmitoylation (F). (G–K) Mutation of palmitoylated Cys residues in Ft results in decreased wing size. Representative wings from wild-type (G), ft4938C/S (H), ft4987C/S (I), and ft2C/S (J) adults. Mutation of Cys4938, Cys4987, or both together leads to undergrowth (K), consistent with activation of Ft. Error bars are mean ± SEM. ***, P < 0.001 (two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test between wild type and each genotype). Bar, 100 µm.