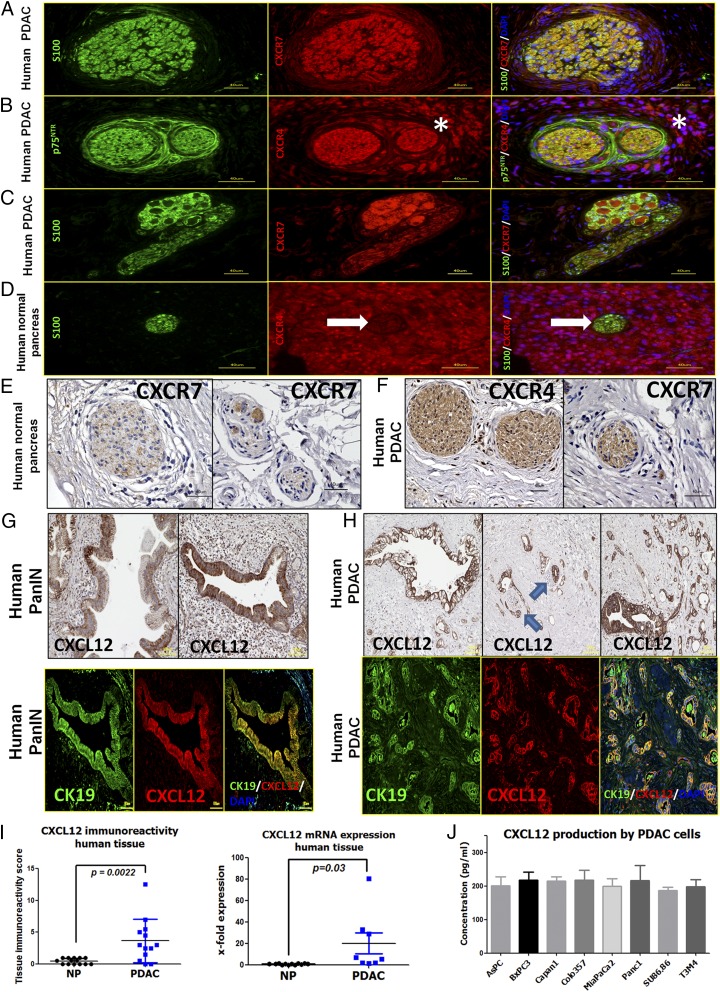
Fig. 2.
SC in human PDAC harbor the chemokine receptors CXCR4 and CXCR7, whereas PanIN lesions and established human PCC lines contain CXCL12. (A–C) Coimmunolabeling of nerves in PDAC tissues with the SC markers S100/p75NTR demonstrates the presence of CXCR4 and CXCR7 in nerves (A and B) and also in intrapancreatic ganglia (C). The asterisks indicate the immunostained perineural inflammatory cells. (D and E) In normal human pancreas the chemokine receptors are only faintly detectable in SC. The white arrow points to the nerve embedded in the exocrine tissue. (F) However, several nerves in PDAC tissues exhibited immunoreactivity for CXCR4 and CXCR7. (G and H) Immunolabeling of PDAC tissues against CXCL12 and colabeling with the PCC marker CK19 revealed PanIN lesions (G) and PCC (H) as the major source of this chemokine in PDAC. The blue arrows point to nerves that are invaded by CXCL12-expressing cancer cells. (I) Accordingly, the mean immunoreactivity of PDAC tissues for CXCL12 (Left) and the mean tissue CXCL12 mRNA expression (Right) was prominently greater in PDAC than in NP. For the mRNA expression, the levels of NP tissues were normalized to 1 (Mann–Whitney u test). (J) Human PCC lines synthesize substantial amounts of CXCL12 as detected via ELISA. Experiments were repeated three times. (Scale bars: A–F, 40 μm; G–H, 100 μm.)