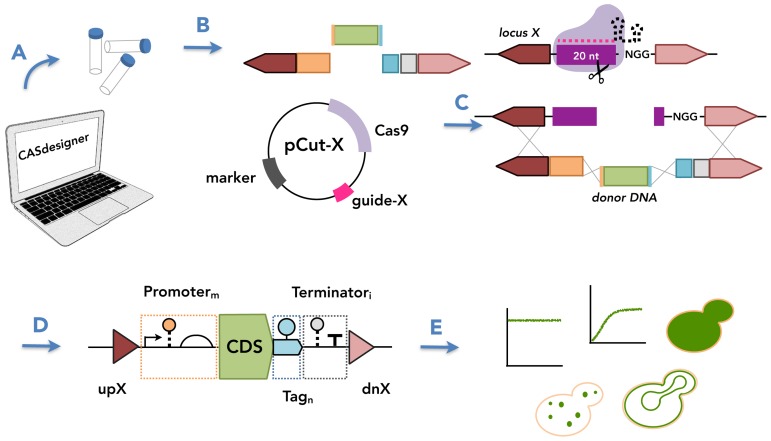
Figure 1.
Cas9-based toolkit for programming gene expression in S. cerevisiae. The toolkit facilitates strain construction by providing characterized genetic parts that can be used to program gene expression. (A) CASdesigner web-based software assists the researcher in selecting genetic parts based on the data reported herein and automatically designs the primers required to (B) generate donor DNA fragments with 30–60 bp inter-fragment and 1 kbp chromosomal homology. The homology regions and a Cas9–sgRNA plasmid (pCut-X) together specify the chromosomal integration site. (C) The sgRNA contains a 20-nt guide sequence also present in the targeted chromosomal locus (cut site). The cut site is cleaved by the sgRNA–Cas9 complex, then repaired by donor DNA via HR. (D) The choice of parts can confer different biological activities, here represented using Synthetic Biology Open Language (SBOL) Visual glyphs (triangles, HR regions; half-circle, ribosome binding site; pentagons pointing to the right, protein-coding sequences; T, terminator; arrow, promoter; circle connected by dashed line, RNA stability element; circle connected by solid line, protein stability element) following established conventions (52). (E) By the choice of genetic parts, a gene of interest can be expressed under various expression programs (level, timing, subcellular localization).