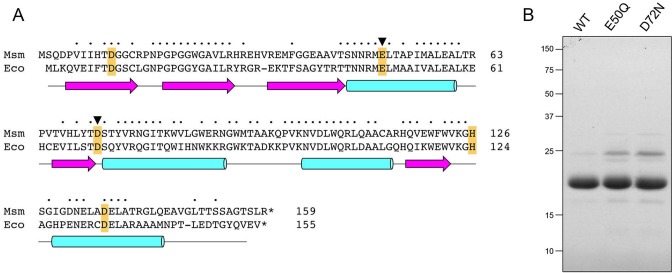
Figure 1.
Recombinant RnhA. (A) Primary structure. The amino acid sequence of M. smegmatis (Msm) RnhA is aligned to that of E. coli (Eco) RNase H1. Positions of side chain identity/similarity are denoted by dots above the residues. Gaps in the alignments are denoted by dashes. Five conserved acidic residues—Asp11, Glu50, Asp72, His126 and Asp136 in RnhA—that are predicted to coordinate two catalytic metal ions in the active site are highlighted in gold shading. The Glu49 and Asp72 residues that were mutated are denoted by black arrowheads. The secondary structure elements of the E. coli RNase H1 crystal structure (24; pdb 1RNH) are displayed below the amino acid sequence, with β-strands as magenta arrows and α-helices as cyan cylinders. (B) Purification. Aliquots (5 μg) of recombinant wild-type RnhA (WT) and mutants E50Q and D72N were analyzed by SDS-PAGE. The Coomassie Blue-stained gel is shown. The positions and sizes (kDa) of marker polypeptides are indicated on the left.