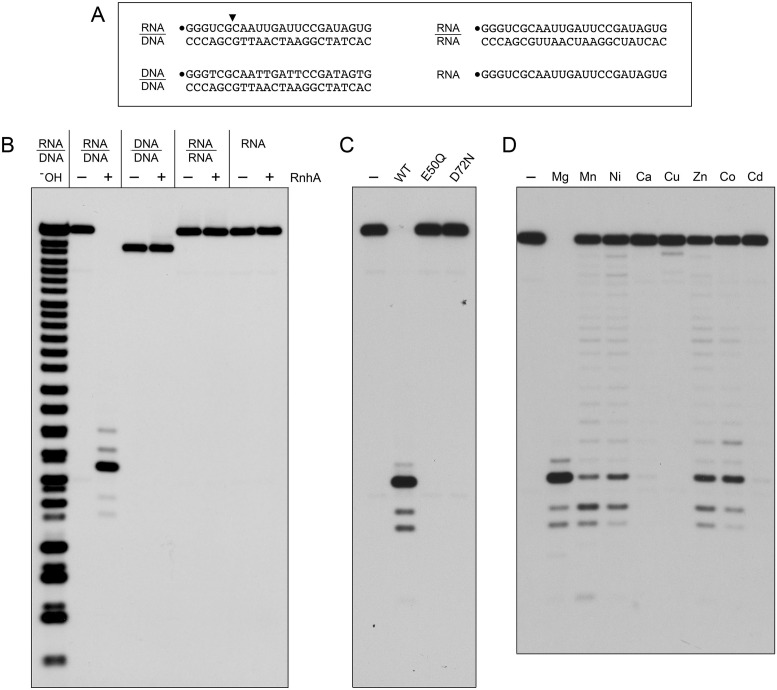
Figure 2.
Metal-dependent RNase H activity and nucleic acid substrate specificity of RnhA. (A) Substrates. The 32P-RNA:DNA, 32P-DNA:DNA and 32P-RNA:RNA duplexes and the 32P-RNA single strand substrates are shown, with the 5′ 32P-label denoted by •. The principal site of RnhA incision of the RNA:DNA hybrid is indicated by a black arrowhead above the 32P-labeled RNA strand. (B) Nucleic acid substrate specificity. Reaction mixtures (10 μl) containing 25 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 50 mM NaCl, 5 mM MgCl2, either 20 nM (200 fmol) 32P-RNA:DNA, 32P-DNA:DNA or 32P-RNA:RNA duplexes or 20 nM (200 fmol) 32P-RNA single strand, and 8 nM (80 fmol) RnhA (where indicated by +) were incubated at 37°C for 20 min. The reactions were quenched with an equal volume of 90% formamide, 50 mM EDTA, 0.3% bromophenol blue. The reaction products were analyzed by electrophoresis through a 40-cm 18% polyacrylamide gel containing 7 M urea in 45 mM Tris-borate, 1 mM EDTA. An alkaline hydrolysis ladder of the 32P-labeled 24-mer RNA strand was analyzed in parallel in lane –OH. The radiolabeled RNAs were visualized by autoradiography. (C) Active site mutations. Reaction mixtures (10 μl) containing 25 mM Tris–HCl (pH 7.5), 50 mM NaCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 20 nM (200 fmol) 32P-RNA:DNA hybrid duplex, and 8 nM (80 fmol) of wild-type RnhA, RnhA-E50Q or RnhA-D72N were incubated at 37°C for 20 min. RnhA was omitted from a control reaction in lane –. (D) Metal cofactor requirement. Reaction mixtures (10 μl) containing 25 mM Tris–HCl, pH 7.5, 50 mM NaCl, 20 nM 32P-RNA:DNA hybrid duplex, 8 nM wild-type RnhA, and 5 mM of the indicated divalent cation (as the chloride salt) were incubated at 37°C for 20 min. Divalent cation was omitted from a control reaction in lane –.