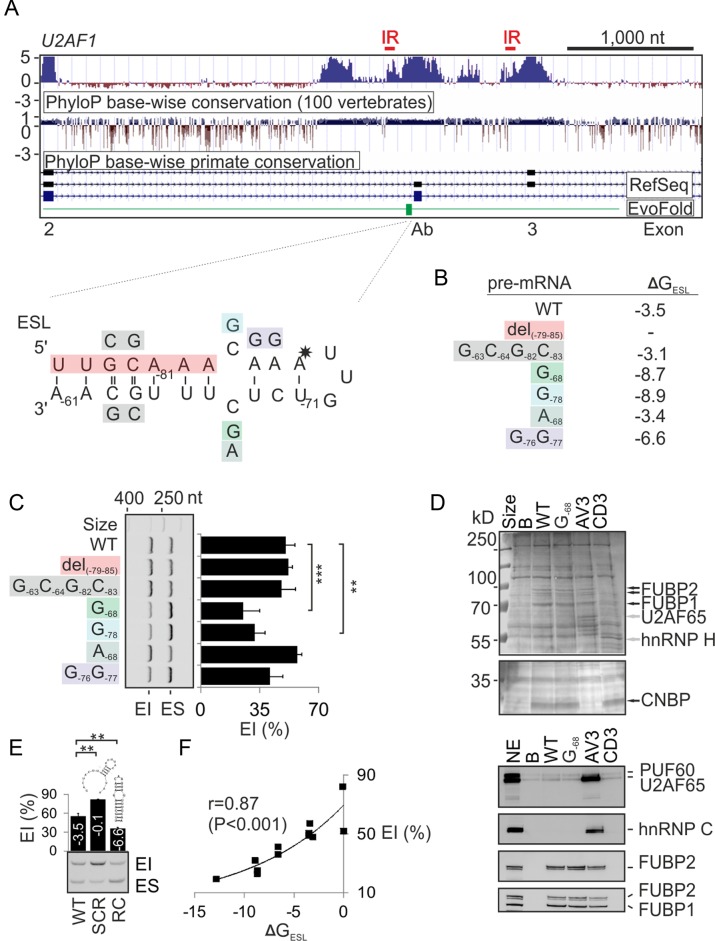
Figure 3.
Internal loop of the predicted ultraconserved hairpin upstream of the BP cluster controls exon Ab inclusion. (A) Sequence conservation across alternatively spliced U2AF1 exons Ab and 3. PhyloP conservation UCSC tracts are followed by the RefSeq annotation of U2AF1 exons (numbered at the bottom). ESL (in green) is expanded in the lower panel; mutations are colored. ESL nucleotide positions are numbered according to their distance from the 3′ss of exon Ab. Asterisk indicates an A>G substitution conserved in many tetrapods (Supplementary Figure S5) and predicted to stabilize the hairpin. Red horizontal bars at the top denote location of the longest inverted repeats (IR) in the conserved regions (Supplementary Figure S9). (B) Predicted free energies (ΔGESL) of the wild-type (WT) and mutant RNAs (kcal/mol). (C) Exon inclusion levels of ESL-mutated pre-mRNAs. Columns represent means and error bars SDs of two transfections of the Ab reporter (Figure 1D). (D) RNA pull-down assay (upper panel) and immunoblots with the indicated antibodies (lower panel). B, beads only, G-68, mutated synthetic RNA (Supplementary Table S1). AV3 and CD3 are control RNAs described previously (19,35). NE, nuclear extract. CNBP (also known as ZNF9) is a CCHC-type zinc finger nucleic acid binding protein identified by mass spectrometry. (E) Exon inclusion (%) in the mRNA from WT and mutated Ab constructs. Scrambled (SCR) and reverse complement (RC) sequences were gactacttttctacttacaggataa and ttgcaaagagacaatttgtttgcaa, respectively. Their predicted energies (kcal/mol) and schematic secondary structures are as indicated. (F) Positive correlation between predicted ΔGESL and exon Ab inclusion levels of 11 different ESL reporters.