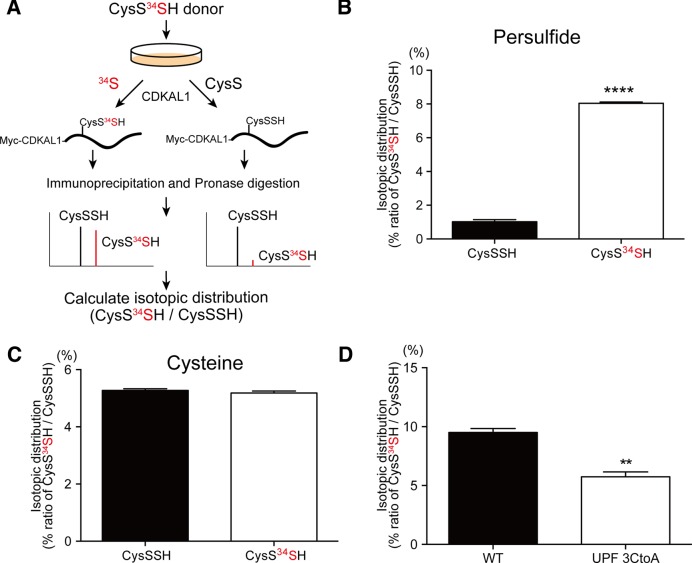
Figure 5.
CysSSH-mediated polysulfidation of CDKAL1. (A) Experimental design to detect 34S-labeled polysulfide in the CDKAL1 protein. (B and C) HeLa cells overexpressing Myc-CDKAL1 were treated with vehicle (CysSSH donor) or the CysS34SH donor for 1 h. Myc-CDKAL1 was immunoprecipitated and subjected to mass spectrometry to determine the isotopic distribution of polysulfidation in Cys residues. The isotopic distribution of CysSSH (abundance of CysS34SH relative to that of CysSSH) is shown in (B). The isotopic distribution of the Cys residue (abundance of CysS34H relative to that of CysSH) is shown in (C). ****P < 0.0001, n = 4. (D) HeLa cells expressing wild-type Myc-CDKAL1 or mutant CDKAL1 carrying Cys-to Ala mutations in the UPF0004 domain were treated with the CysS34SH donor, followed by mass spectrometric analysis. The mutant CDKAL1 had less 34S incorporation in Cys residues in CDKAL1, when compared with the wild-type CDKAL1. n = 3 each, **P < 0.01.