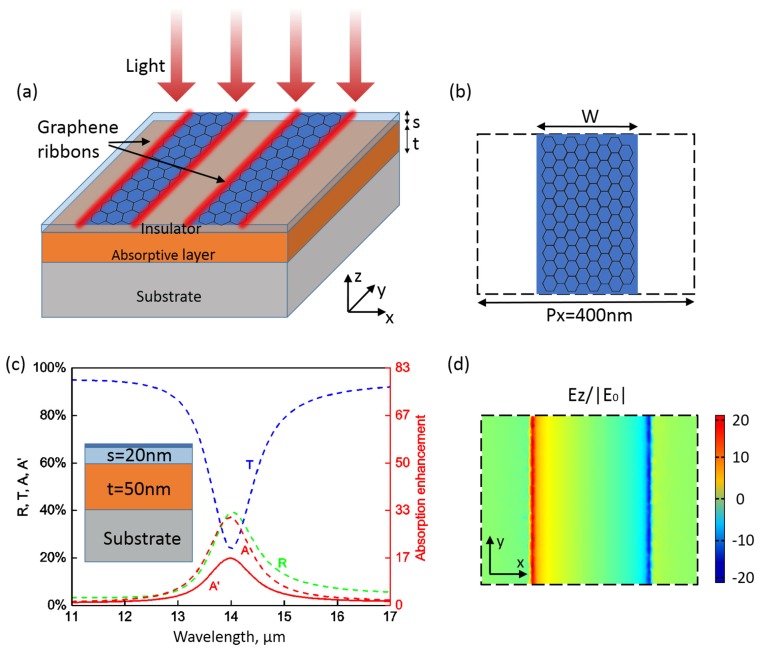
Figure 1.
Plasmonic light trapping with graphene nanoribbon structure. (a) Schematic of the proposed structure. From the top to the bottom of the structure are a nanostructured graphene film with an array of periodical nanoribbons, an insulator layer with a thickness of s, an absorptive layer with a thickness of t, and a semi-infinite substrate, respectively. Incident light of transverse-magnetic (TM) (x-polarized) modes excites localized plasmons in the doped graphene layer, which trap light in the near-field and enhance the optical absorption in the light-absorbing layer underneath; (b) A graphene nanoribbon with geometric parameters. The period of the graphene nanoribbon is nm. The width is W; (c) Simulated spectra of reflection (R), transmission (T), total absorption (A), and absorption in the absorptive layer () for TM mode under normal incidence. The Fermi energy is eV. The enhancement of absorption in the absorptive layer is also shown; (d) Electric field distributions in the z-direction at the resonance wavelength of m. The field is normalized to the field amplitude of the incident light () and plotted in the x–y plane that is 5 nm above the graphene nanoribbons.