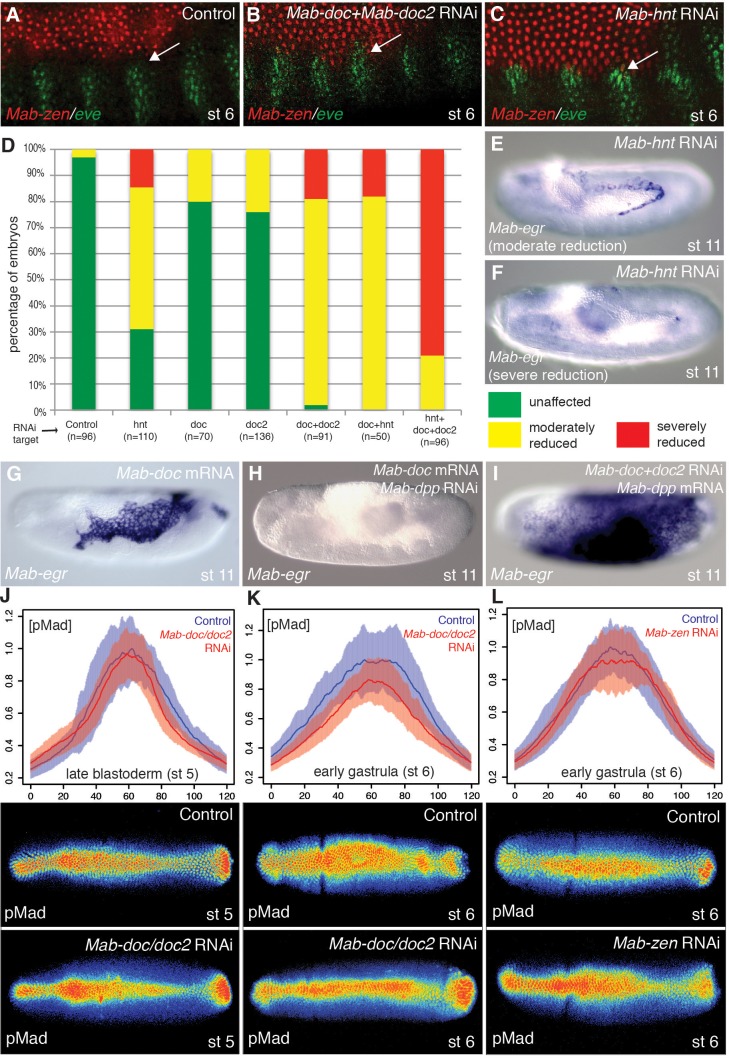
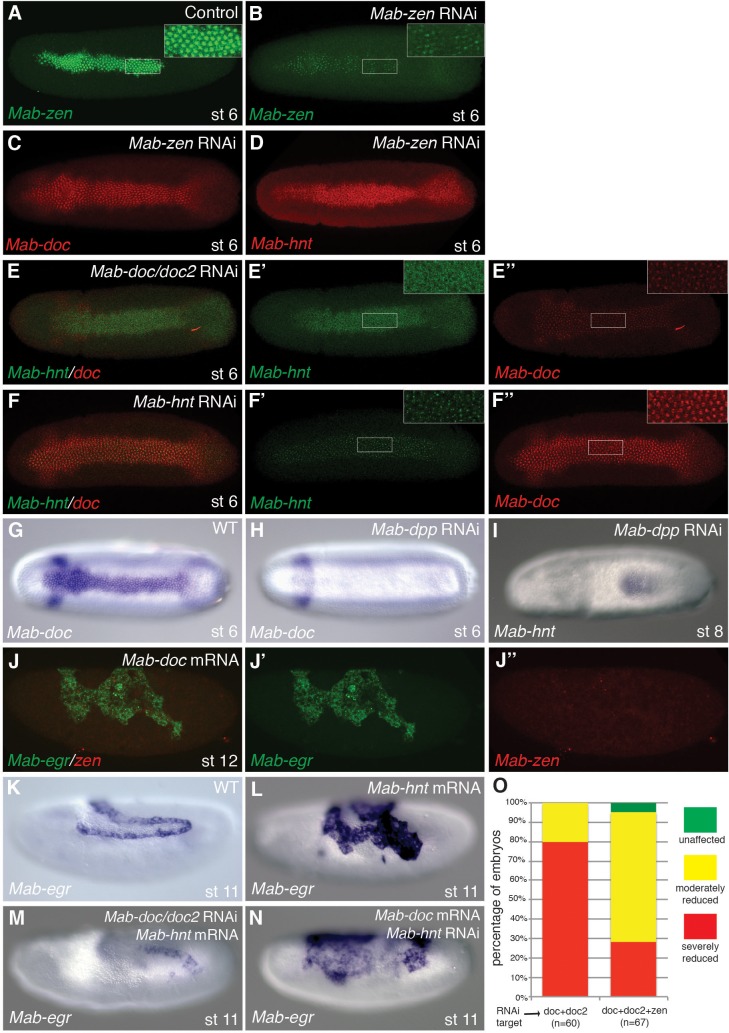
Figure 3. Mab-doc and Mab-hnt elevate BMP signaling to specify amnion in Megaselia.
(A–C) Mab-zen and Mab-eve expression in early gastrula control embryo (A) and after Mab-doc/doc2 knockdown (B) or Mab-hnt knockdown (C). Arrows, gap between the Mab-eve and Mab-zen domains (A) that is suppressed in the knockdown embryos (B, C). (D–F) Bar chart (D) quantifying the reduction of Mab-egr expression at stage 11/12 after Mab-hnt and/or Mab-doc/doc2 knockdown, and representative embryos of moderately reduced (yellow, E), or severely reduced (red, F) phenotypes. (G–I) Mab-egr expression at germ band extension following Mab-doc overexpression (G), Mab-doc overexpression and Mab-dpp knockdown (H), and Mab-dpp overexpression and Mab-doc/doc2 knockdown (I). (J–L) Mean and shaded standard deviation of pMad intensities in control injected embryos (blue) and in Mab-doc/doc2 knockdown embryos (red) at the cellular blastoderm stage (n = 10, control n = 10) (J), at early gastrulation (n = 11, control n = 11) (K), and in Mab-zen knockdown embryos (red) at early gastrulation (n = 10, control n = 17) (L) with representative embryos stained for pMad underneath each plot.