Fig. 2.
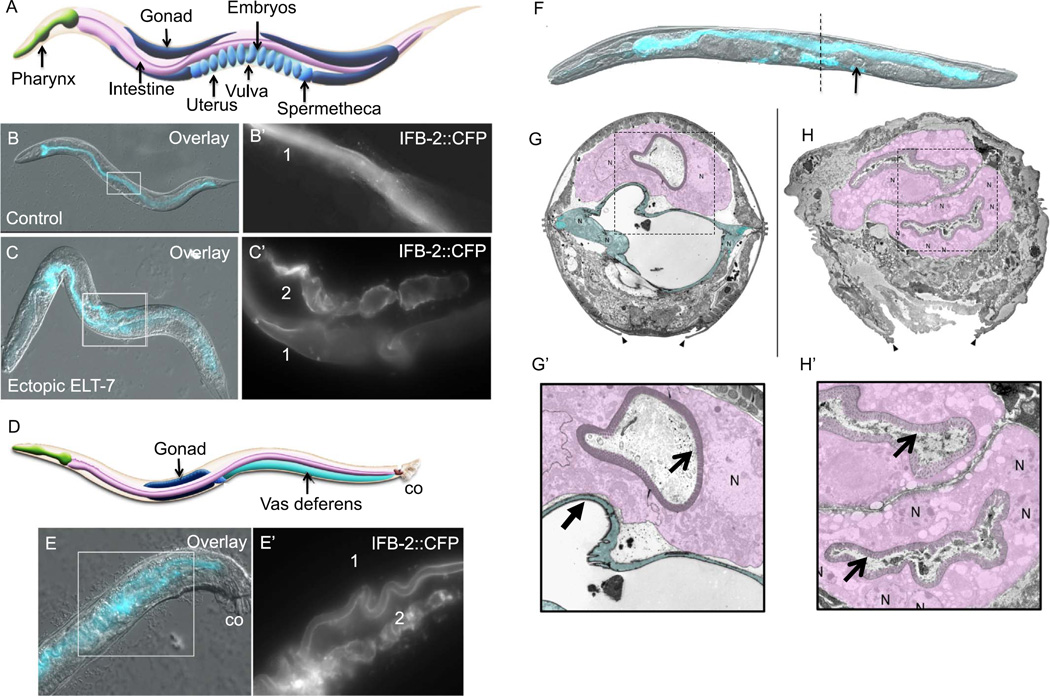
Transorganogenesis of the somatic gonad into intestine. (A) Diagram of adult C. elegans hermaphrodite (approximately 1 mm in length) showing the neuromuscular pharynx, intestine, and the two “U” shaped gonad arms that are connected by two spermathecae and a uterus. (B, B’) Expression and localization of intestine-specific intermediate filament protein (IFB-2::CFP) that lines the single intestinal lumen “1” in an adult hermaphrodite. (C, C’) IFB-2::CFP expression 48 h after a 15-min pulse of ELT-7 expression at the L4 stage. Additional IFB-2-lined lumen “2” is seen in the uterus. (D) Diagram of adult C. elegans male (approximately 0.8 mm in length) showing the vas deferens (co; copulatory organ). (E, E”) IFB-2::CFP in a male 48 h after brief ectopic ELT-7 expression. IFB-2 expression is visible in the intestine “1” and vas deferens “2”. (F) Hermaphrodite 48 h after ectopic ELT-7 induction at the L4 stage (DIC and CFP overlay). An embryo is retained in one spermatheca (arrow). Dotted line indicates approximate transverse section of micrograph shown in H. (G) Transmission electron micrograph of a transverse section at the vulva of an L4 stage hermaphrodite (intestine is shaded purple and uterus is shaded blue, arrowheads point to the edges of the vulval opening, N, cell nucleus). (H) Transmission electron micrograph of a transverse section at the vulva of an L4 stage hermaphrodite 48 h after ectopic ELT-7 expression; the two intestine-like epithelial tubes are shaded in purple. The normal intestine (upper epithelial tube) shows 1–2 nuclei per cross-section, but the converted uterine tissue, which is derived from many more cells, shows many nuclei. (G’, H’) Magnified region of micrographs in G and H showing the smooth lumen of the uterus (closed arrow) and rough intestinal lumen that is lined with microvilli (open arrows).
Cartoons are reprinted with permission from Altun and Hall (2009) (www.wormatlas.org).