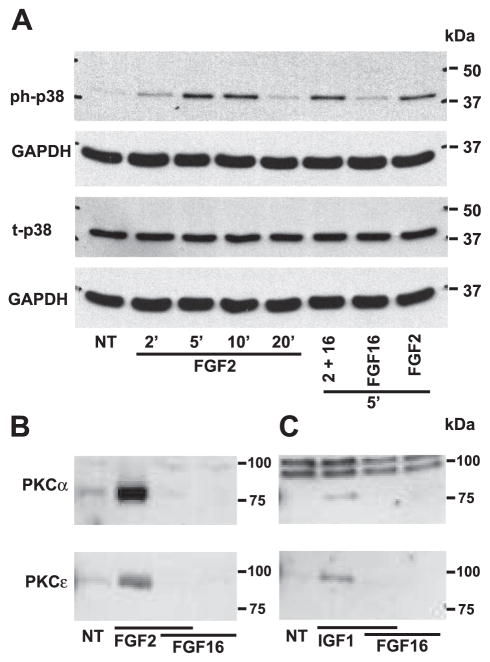
Fig. 5.
FGF-16 modulates signal transduction in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. A: cells were treated with 1 ng/ml FGF-2 for 2, 5, 10, and 20 min, or 1 ng/ml FGF-2 and 100 ng/ml FGF-16 for 5 min, or 100 ng/ml FGF-16 alone for 5 min. Cell extracts were analyzed by protein immunoblotting for phosphorylated p38 MAPK (ph-p38) and total p38 (t-p38), and each blot was stripped and reprobed with GAPDH as a control for gel loading. B: membrane (sarcolemmal) fractions from cells treated with FGF-2 (1 ng/ml) and/or FGF-16 (100 ng/ml) for 5 min were assessed by protein immunoblotting for PKC-α (80 kDa) or PKC-ε (90 kDa). C: same experiment as in B except for growth factor treatment with IGF-1 (10 nM) and/or FGF-16 (100 ng/ml) for 2 min. NT, no treatment. Positions of molecular mass markers (kDa) are shown at right.