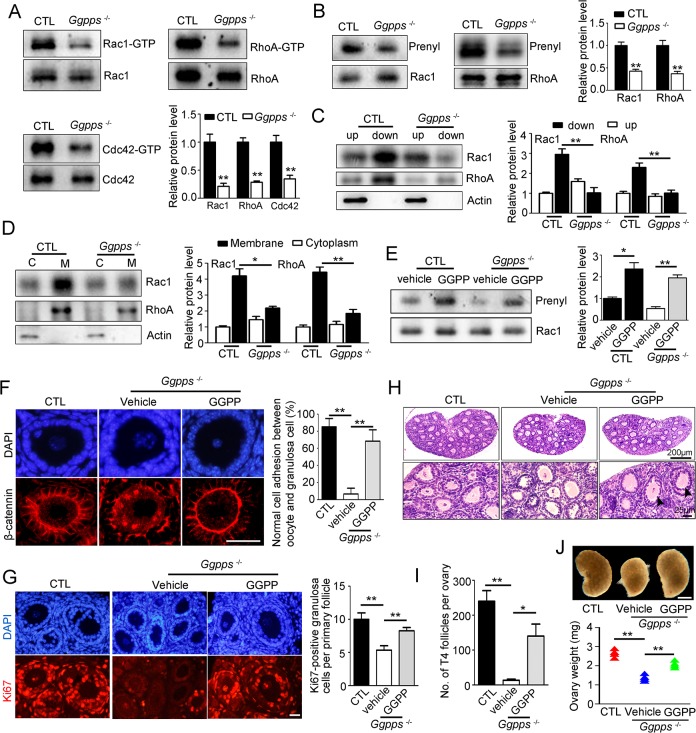
Fig 6. GGPP depletion disrupts cadherin-mediated cell contact by inhibiting Rho GTPase geranylgeranylation and GTPase activity.
(A) The enzymatic activity of Rac1, RhoA, and Cdc42 in PD 12–14 ovaries. (B) The prenylation of Rac1 and RhoA in PD 12–14 ovaries. (C) Subcellular fractionation of Rac1 and RhoA in PD 12–14 ovaries was conducted using the Triton X-114 partition method. The aqueous upper phase contained the water-soluble small GTPases, and the lower organic phase contained the lipid-soluble small GTPases. (D) Rac1 and RhoA membrane association, as determined using ultracentrifugation, in PD 12–14 ovaries. (E) Rac1 prenylation in organ-cultured PD 12–14 ovaries by GGPP treatment (20 μM, 24 h). (F) β-catenin immunofluorescence in the primary follicles of PD 13 ovaries 5 days after daily intraperitoneal injections of GGPP (2 mg/kg). (G) Ki67 immunofluorescence, H&E staining (H), quantification of the T4 follicles (I) and ovary weight (J) in PD 13 ovaries after 5 days of daily intraperitoneal injections of GGPP (2 mg/kg). Data were presented as the mean ± SEM. *p<0.05, **p<0.01.