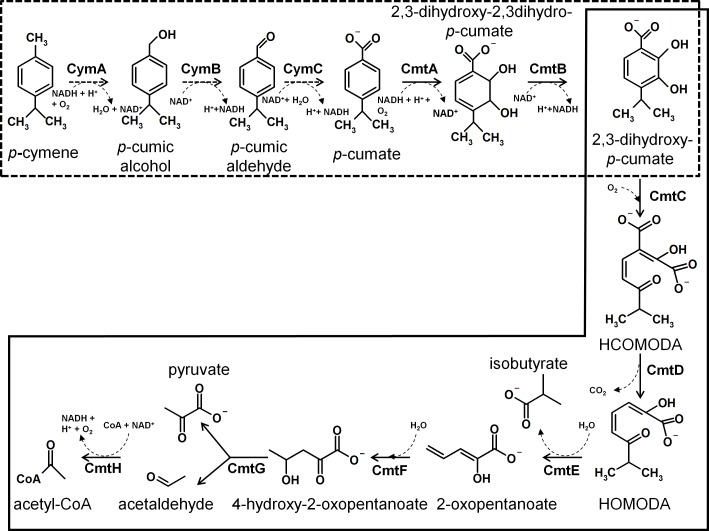
Fig 2. Model of p-cymene and 2,3-dihydroxy-p-cumate catabolic pathways in B. xenovorans LB400.
The box with dotted border indicates the p-cymene peripheral pathway, which converts p-cymene into 2,3-dihydroxy-p-cumate. The substrate is p-cymene and the products are p-cumic alcohol, p-cumic aldehyde, p-cumate, 2,3-dihydroxy-2,3dihydro-p-cumate and 2,3-dihydroxy-p-cumate. The enzymes are CymA (p-cymene monooxygenase), CymB (p-cumic alcohol dehydrogenase) CymC (p-cumic aldehyde dehydrogenase), CmtA (p-cumate dioxygenase) and CmtB (2,3-dihydroxy-2,3-dihydro-p-cumate dehydrogenase). The reactions of the 2,3-dihydroxy-p-cumate central pathway are presented in a box with continuous border. The substrate is 2,3-dihydroxy-p-cumate and the final products are isobutyrate, pyruvate and acetyl-CoA. The enzymes are CmtC (2,3-dihydroxy-p-cumate-3,4-dioxygenase), CmtD (2-hydroxy-3-carboxy-6-oxo-7-methylocta-2,4-dienoate decarboxylase), CmtE (2-hydroxy-6-oxo-7-methylocta-2,4-dienoate hydrolase), CmtF (2-hydroxypenta-2,4-dienoate hydratase), CmtG (4-hydroxy-2-pentanoate aldolase) and CmtH (acetaldehyde dehydrogenase).