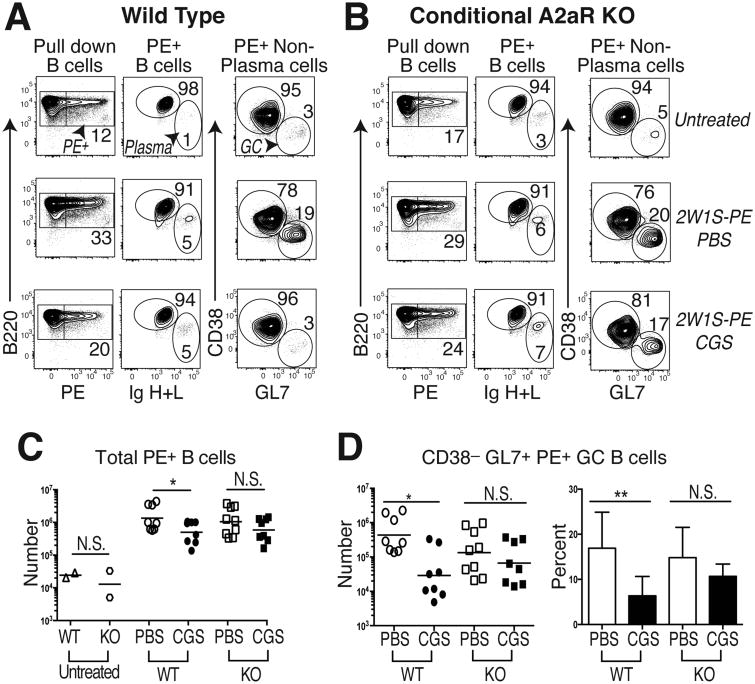
Figure 4. T cell A2aR activation reduces GC B cell immunity.
PE-specific B cells were enriched from the spleen and LNs of 2W1S-PE primed WT or CD4-Cre Adora2af/f conditional knock-out (KO) mice given a 7d course of CGS or the PBS vehicle alone. (A) Gating strategy to identify PE-specific B220+ total B cells (left column), B220intermediate intracellular Ig (H+L)hi plasma cells (middle column), as well as intracellular Ig (H+L)intermediate CD38– GL7+ GC B cells (right column) in control untreated (upper row), 2W1S-PE immunized and PBS-treated (middle row), and 2W1S-PE immunized and CGS-treated (lower row) WT mice. (B) Representative KO mice treated as in (A). (C) Absolute numbers of total PE-specific B cells in WT and KO mice treated as in (A) and (B), with untreated mice shown as a control. (D) Absolute numbers and frequency of PE-specific polyclonal CD38– GL7+ GC B cells in immunized WT and KO mice treated as in (A) and (B). Data are representative of three independent experiments (n=8-9 mice). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001