Table 1.
Reaction optimization.
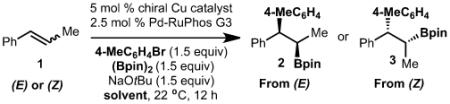
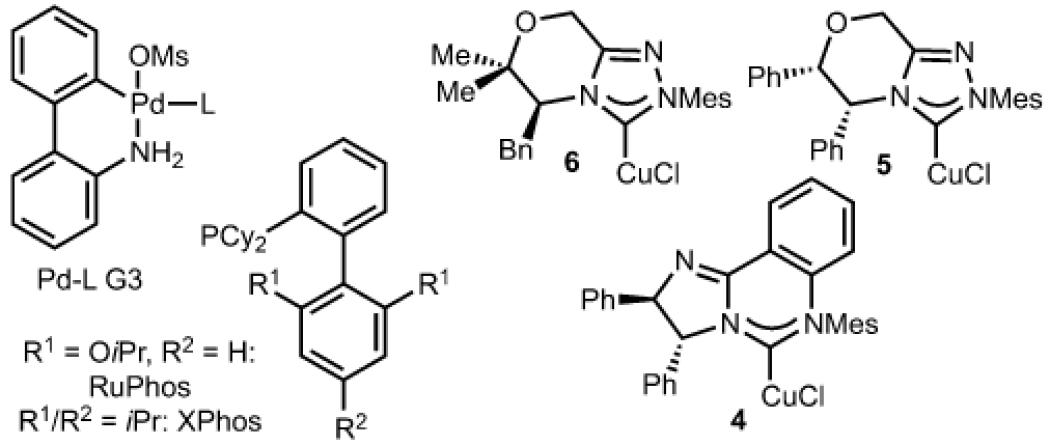
| Entry | (E)/(Z) | Copper catalyst |
Solvent | Yield [%][a] | d.r.[b] | e.r.[c] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | (E) | 4 | THF | 45 | 15:1 | 70:30 |
| 2 | (E) | 5 | THF | 32 | 5:1 | 82:18 |
| 3 | (E) | 6 | THF | 32 | 9:1 | 43:57 |
| 4 | (Z) | 4 | THF | 46 | 11:1 | 91:9 |
| 5 | (Z) | 5 | THF | <5 | – | – |
| 6 | (Z) | 6 | THF | <5 | – | – |
| 7 | (Z) | 4 | toluene | 68 | 8:1 | 90:10 |
| 8 | (Z) | 4 | toluene:THF (10:1) |
78 | 15:1 | 94:6 |
| 9 | (Z) | 4 | toluene:Et20 (10:1) |
26 | 6:1 | 86:14 |
| 10 | (Z) | 4 | toluene:DMF (10:1) |
58 | 16:1 | 95:5 |
| 11 | (Z) | 4 | toluene:MeCN (10:1) |
83 | 50:1 | 96:4 |
| ||||||
Yield was determined by gas chromatography (GC) analysis with a calibrated internal standard.
Diastereomeric ratio (d.r.) was determined by GC analysis of the unpurified reaction mixture.
Determined by HPLC (with a chiral column) of the purified products. Solvent key: tetrahydrofuran (THF); diethyl ether (Et2O); N,N,-dimethylformamide (DMF); acetonitrile (MeCN).
