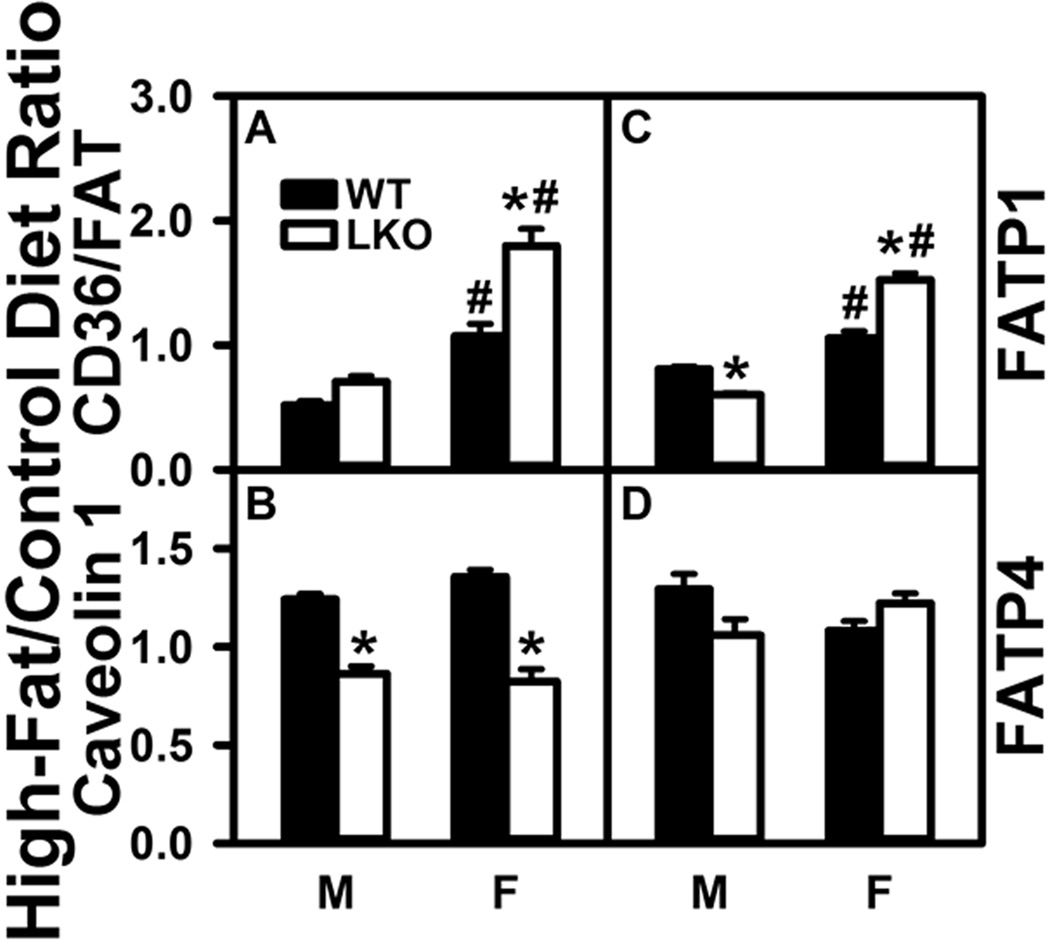
FIGURE 5.
Impact of Fabp1 gene ablation (LKO) differentially alters the ability of high fat diet (HFD) to impact brain protein levels of membrane proteins involved in fatty acid uptake. All conditions were as described in Figure 1 except that SDS-PAGE followed by western blotting on aliquots of brain homogenate as described in Materials and Methods to determine levels of: (A) CD36/FAT (β-actin), (B) CAV1 (β-actin), (C) FATP1 (GAPDH), and (D) FATP4 (β-actin). Relative protein levels were normalized to gel-loading control protein (β-actin or GAPDH), values compared to male WT set to 1, results expressed as the relative ratio of each protein in High-Fat/Control diet, and data shown as mean ± SEM (n = 8); *, P < 0.05 for LKO vs WT; #, P < 0.05 for female (F) vs male (M).