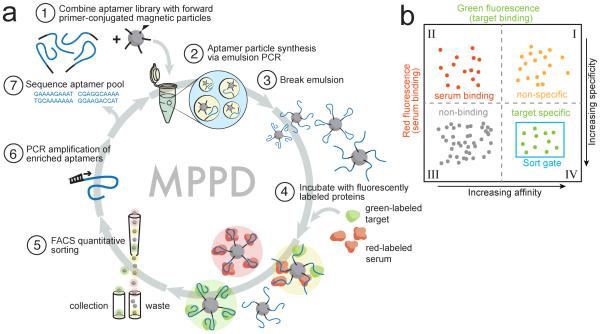
Figure 1. Overview of MPPD.
(a) We transform solution-phase aptamers into aptamer particles by covalently conjugating forward PCR primers to magnetic particles (1) and performing emulsion PCR (2) under conditions that produce monoclonal aptamer particles displaying many copies of a single sequence (3). These particles are incubated with target and non-target proteins labeled with distinct fluorophores (green and red, respectively) (4), then sorted using FACS (5) to isolate aptamers that exhibit high affinity and specificity. These aptamers are then PCR amplified for additional screening (6) or sequenced for further characterization (7). (b) Aptamer particles are sorted with two-dimensional FACS to selectively isolate aptamers with high green (high affinity) and low red (high specificity) fluorescence.