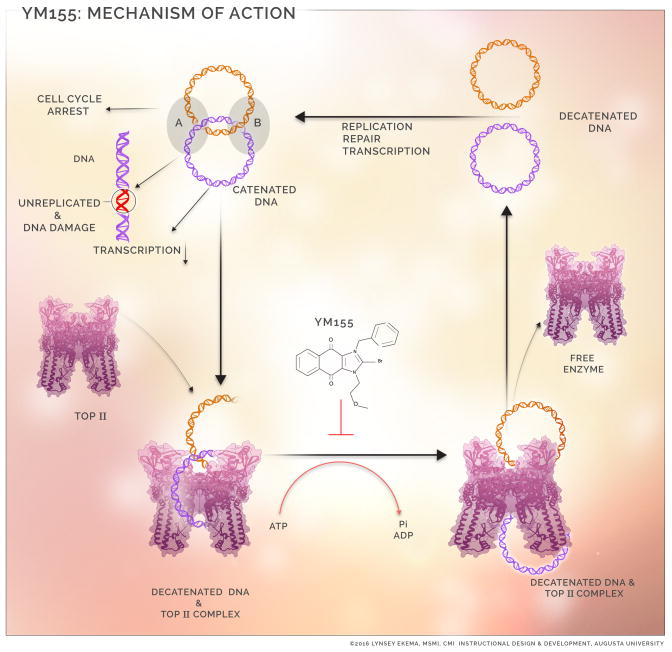
Figure 6.
Schematic description of the mechanism of action of YM155. Catenated DNAs are frequently encountered during DNA replication, repair, transcription and chromosomal separation. Continued presence of such sends signals through checkpoint cascade resulting in cell cycle arrest, unreplicated/damaged DNA, decreased DNA transcription and unseparated chromosome. Progression of the above processes depend on prompt resolution of catenated DNA at junction A and B. YM155 impairs TOP2α mediated DNA decatenation.