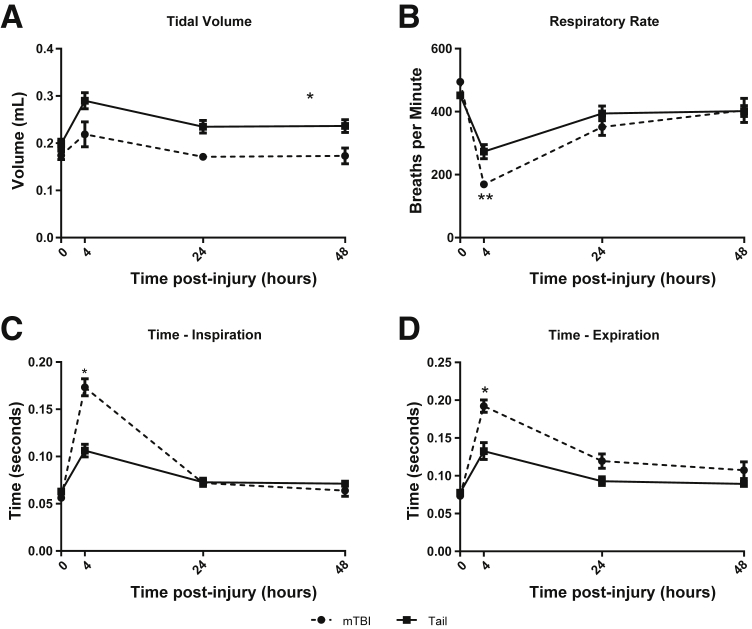
Figure 3.
Pulmonary physiology measured by whole-body plethysmography. Both groups of trauma show similar respiratory parameters by 48 hours after trauma. A: Mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI) mice had lower tidal volumes overall but showed the same trend as tail trauma while returning to their baseline level by 24 hours. Respiratory rate (B), time of inspiration (C), and time of expiration (D), were significantly different between groups only at the 4-hour time point, but normalized by 24 hours. Data were obtained by unrestrained whole-body plethysmography at the time points indicated. Data are shown as means ± SEM. n = 5 for mTBI; n = 8 for tail. ∗P < 0.001, ∗∗P < 0.01 tail trauma compared with mTBI.