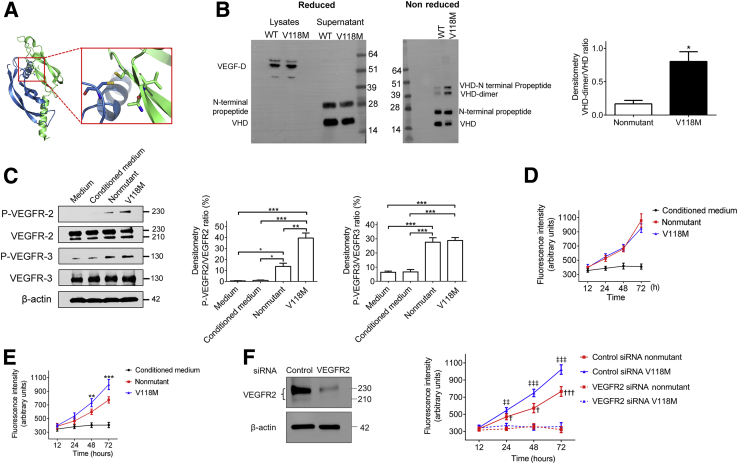
Figure 3.
Effects of nonmutant VEGF-D and VEGF-DV118M. A: Two molecules of the VEGF-D receptor pack in the crystal lattice of 2XV7 with an extensive dimeric interface, which has buried surface area of 2370 Å2. Inset: A close-up of the boxed area, on the dimeric interface with Val 118 in the immediate vicinity of other residues that modulate the dimeric interaction. B: Constructs expressing VEGF-DV118M or nonmutant VEGF-D were transfected into human embryonic kidney 293 (HEK293) cells. VEGF-D protein expressions were validated by Western blot. Left panel: Under reducing conditions, both nonmutant and VEGF-DV118M were present as a full-length form in the lysates of stable transfected cells. In cell culture supernatants from both nonmutant and mutated VEGF-D plasmid transfected HEK293 cells, two forms of VEGF-D were identified: VEGF-D cleaved at the C-terminal regions (upper bands) and VEGF homology domain (VHD; lower bands). Under nonreducing conditions, VEGF-DV118M in cell culture supernatants formed significantly more dimers compared to the nonmutant protein. Right panel: Quantification of the ratio of VHD dimers/VHD monomer. C: Human umbilical vein endothelial cells were incubated with concentrated conditioned medium from stable transfected HEK293 cell lines containing equal amounts of nonmutant and VEGF-DV118M (final VEGF-D concentration, 1 μg/mL). Left panel: Phosphorylation of VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3 was detected after 30 minutes. Middle and right panels: Quantification of the ratio of p-VEGFR-2/total VEGFR-2 and p-VEGFR-3/total VEGFR-3, respectively. Cell proliferation assay of human lung lymphatic endothelial cells (D) and aortic endothelial cells (HAECs; E) treated with concentrated conditioned medium from stable transfected HEK293 cell lines containing equal amounts of nonmutant and VEGF-DV118M (final VEGF-D concentration, 1 μg/mL). Data represent results of three independent experiments. F: HAECs were transfected with control siRNA or VEGFR-2 siRNA for 48 hours and subsequently incubated with concentrated conditioned medium from stable transfected HEK293 cell lines containing equal amounts of nonmutant and VEGF-DV118M (final VEGF-D concentration, 1 μg/mL). Left panel: Efficiency of siRNA-mediated knockdown of VEGFR-2 was confirmed by Western blotting. Right panel: Cell proliferation was determined at the indicated time points after treatment with nonmutant or VEGF-DV118M. Data represent at least three independent experiments. Data are means ± SEM (D–F). ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, and ∗∗∗P < 0.001 (t-test or one-way analysis of variance, as appropriate); †P < 0.05, †††P < 0.001 (control versus VEGFR-2 siRNA transfected cells treated with nonmutant VEGF-D by one-way analysis of variance); ‡‡P < 0.01, ‡‡‡P < 0.001 (control versus VEGFR-2 siRNA transfected cells treated with VEGF-DV118M).