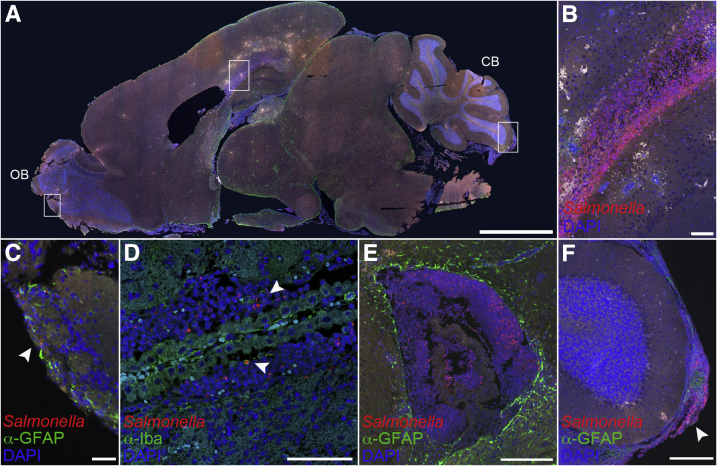
Figure 9.
Bacterial accumulation and macrophage infiltration in the brains of ataxic Nramp1+/+ mice. Brains from mice with clinical signs of ataxia after infection with Salmonella were immunostained. A: Low-magnification image of infected brain tissue immunostained for glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP; green), Salmonella (red), and DAPI (blue). Boxed regions illustrate bacteria in the corpus collosum, olfactory bulb, and meningies and are magnified in B, C, and F, respectively. For orientation purposes, the olfactory bulb (OB) and cerebellum (CB) are labeled. Representative image of Salmonella in the corpus callosum (B), olfactory bulb (C), ventricle (D and E), and cerebellar meninges (F) of a neurological mouse immunostained for either Iba1 or GFAP (green), Salmonella (red), and DAPI (blue). Arrowheads represent intracellular bacteria present in a monocyte (D) and presence of bacterial meningitis (F). Scale bars: 2 mm (A); 100 μm (B–D); 200 μm (E and F).