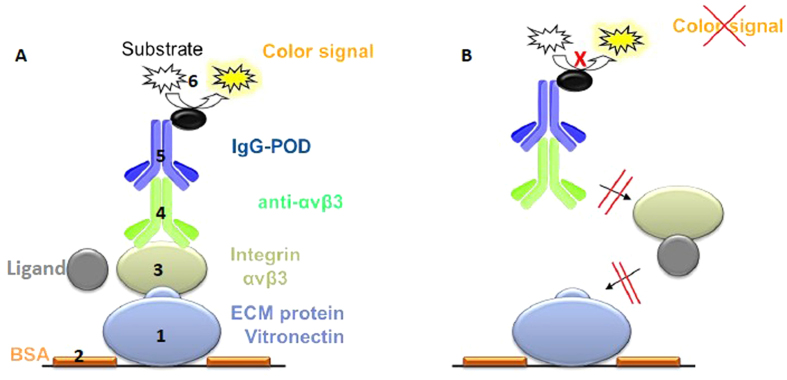
Figure 2. Schematic illustration of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
(A) 1. Each well (96-well plate) is coated with an ECM protein (e.g. vitronectin for αvβ3). 2. Uncoated surface is blocked by bovine serum albumin (BSA). 3. ECM protein competes with the tested ligand for binding to the soluble integrin (e.g. αvβ3). 4. Integrin bound to ECM protein is detected by an integrin-specific primary antibody. 5. Secondary antibody, conjugated with a peroxidase (POD), detects bound primary antibody. 6. Peroxidase converts a colorless substrate into a colored substrate (TMB, 3,3′,5,5′-tetrametylbenzidine). (B) The ligand inhibits binding of the coated ECM protein to the integrin. Consequently, steps 3–6 are blocked and no color signal can be detected.