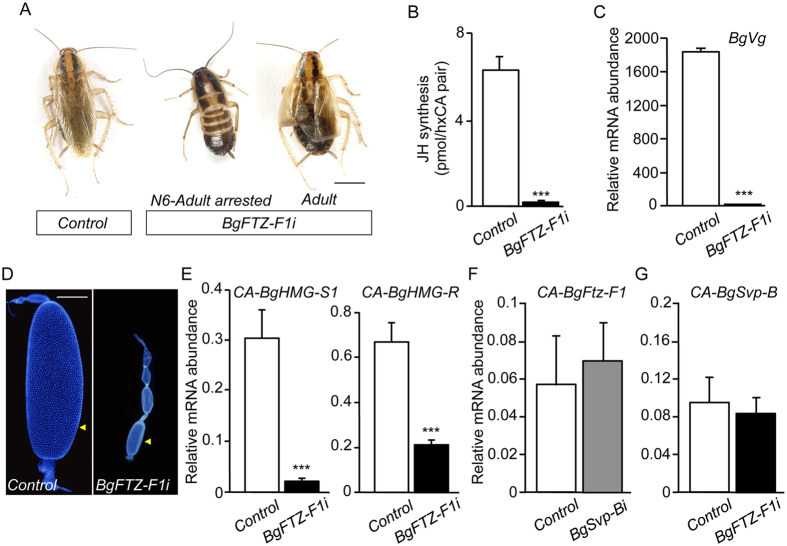
Figure 11. Loss of BgFTZ-F1 impairs JH synthesis in B. germanica adult females.
(A) Newly emerged sixth instar female nymphs were injected with 3 μg of dsMock (Control) or dsBgFTZ-F1 (BgFTZ-F1i). Dorsal views of Control and BgFTZ-F1i animals. BgFTZ-F1i animals either arrested development at the transition between the last nymphal instar and the adult stage (left) or molted properly into adults with only minor problems in the extension of the wings (right). (B) Rates of JH synthesis by CA incubated in vitro from 5-day-old Control and BgFTZ-F1i adult females. (C) BgVg mRNA levels in the fat body of 5-day-old Control and BgFTZ-F1i females, relative to BgActin5C mRNA levels, measured by qRT-PCR. (D) DAPI-stained ovarioles from 5-day-old Control and BgFTZ-F1i adult females. Arrowheads indicate basal oocytes. (E) BgHMG-S1 and BgHMG-R mRNA levels in the CA of 5-day-old Control and BgFTZ-F1i females, relative to BgActin5C mRNA levels, measured by qRT-PCR. (F) BgFTZ-F1 mRNA levels in the CA of 5-day-old Control and BgSvp-Bi females, relative to BgActin5C mRNA levels, measured by qRT-PCR. (G) BgSvp-B mRNA levels in the CA of 5-day-old Control and BgFTZ-F1i females, relative to BgActin5C mRNA levels, measured by qRT-PCR. Error bars indicate the SEM (n = 3–10). Asterisks indicate differences statistically significant (***p ≤ 0.0005, Student’s t-test). Scale bar in (D): 1 mm.