Fig. 1.
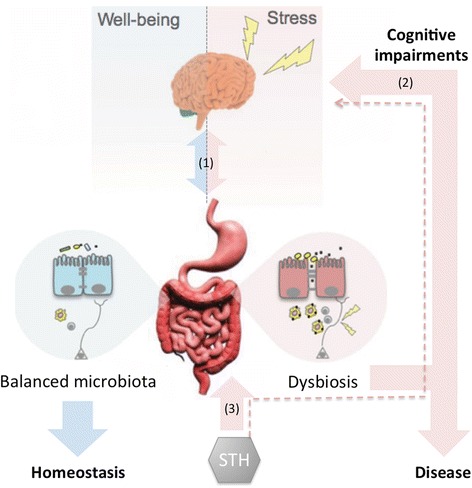
The microbiota-gut-brain axis and its interactions with soil-transmitted helminths (STH): (1) shows the bidirectional communication between the gut and the brain, which occurs through multiple pathways that include hormonal, neural and immune mediators; (2) shows the impact of gut microbiota dysbiosis on cognition; (3) shows the impact of helminth infection on the gut microbiota. The dotted arrow shows the hypothesized pathway leading from STH infection to cognitive impairments, potentially through its impact on the gut microbiota (i.e. dysbiosis). Adapted from De Palma et al. 2014 [65]
