Figure 2.
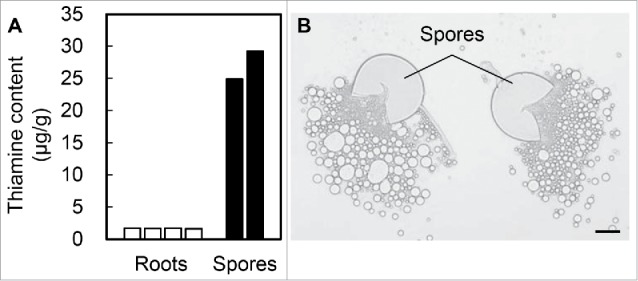
Thiamine content and lipids in the spores of the AM fungus Rhizophagus irregularis. (A) Thiamine content of L. japonicus roots and AM spores was determined using a VitaFast Vitamin B1 kit (Biopharm) that detects thiamine and its phosphate esters. Three-week-old L. japonicus roots and AM spores (DAOM197198; Premier Tech; ca. 40 000 spores) were homogenized and incubated in 71.4 mM citric acid buffer (20 mL; pH 4.5) in the presence of 300 mg Taka-Diastase (Sigma) for 1 h at 37°C, and then for 30 min at 95°C; the solution was then quickly cooled to 30°C and centrifuged at 9200× g for 10 min. The supernatants were passed through 0.22-μm mixed cellulose ester filters. Bioassay was performed according to the manufacturer's instructions. Bar plots represent independent biological replicates. (B) Ruptured AM spores releasing lipids. Scale bar, 50 μm.
