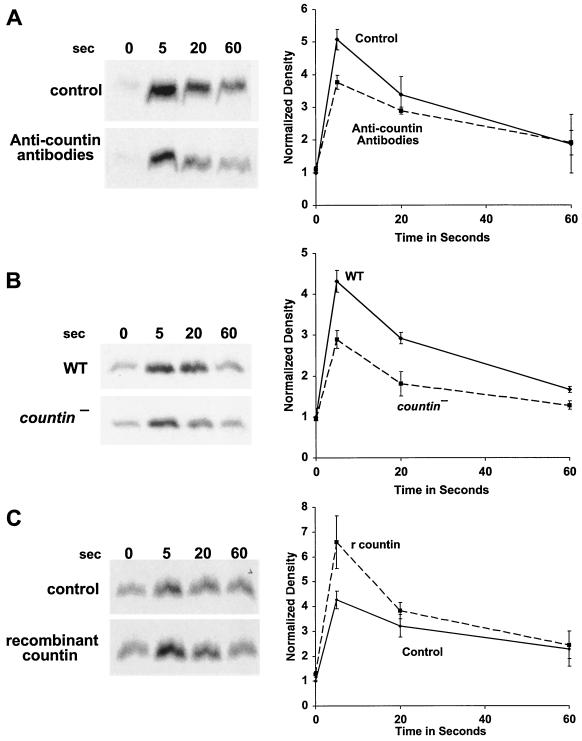
FIG. 3.
Countin potentiates the cAMP-stimulated translocation of Akt/PKB to membranes. (A) Anti-countin antibodies inhibit Akt/PKB translocation to the membrane. Ax4 cells were developed in the presence or absence of anti-countin antibodies, collected at 6 h, and stimulated with cAMP, and then aliquots of cells were filter lysed at the indicated times after stimulation. The membrane fraction was collected and isolated by SDS-PAGE. Western blots stained with anti-Akt/PKB antibodies are shown. The graph shows densitometry of the X-ray films normalized as described for Fig. 1 from four separate experiments. The difference at 5 s was significant (P < 0.05; t test). (B) countin− cells have a reduced Akt/PKB translocation. Akt/PKB translocation to membranes was examined in 6-h-starved countin− cells and parental Ax4 cells (WT). Cells were stimulated with cAMP and processed as described for panel A. The graph shows data normalized as for panel A from four separate experiments. The difference at 5 s was significant (P < 0.01; t test). (C) A 1-min exposure of cells to recombinant countin potentiates Akt/PKB translocation to the membrane. After 6 h of starvation, Ax4 cells were exposed to 200 ng of recombinant countin per ml for 1 min, and then cells were stimulated by cAMP. Samples were treated as above, and Western blots were stained with anti-Akt/PKB antibodies. The graph shows data normalized as described for panel A from four separate experiments. The difference at 5 s was significant (P < 0.05; t test).