FIG. 6.
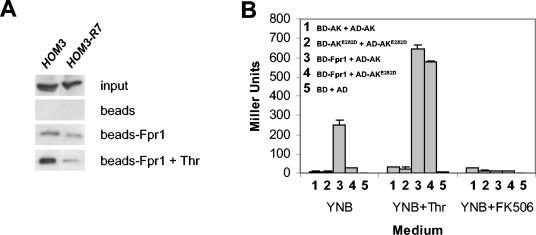
Aspartokinase interacts with itself and FKBP12. (A) FKBP12-AK and AK-AK interaction by in vitro affinity chromatography. Crude protein extracts obtained from a wild-type strain (BY4741) or from a strain expressing the HOM3-R7 mutant allele (MAY315) were incubated with His6-tagged yeast FKBP12 coupled to agarose beads in the presence or absence of 30 mM l-threonine. Bound proteins were eluted and analyzed by Western blotting with antibodies against yeast AK. Binding reactions with agarose beads alone were included as controls. (B) Fpr1-AK and AK-AK interactions in vivo. Transformants from yeast two-hybrid host strain PJ69-4A coexpressing Gal4 DNA-binding domain (BD) fusion proteins from plasmid pGBT9-Fpr1 (BD-Fpr1), pGBT9-AK (BD-AK), or pGBT9-AK(E282D) (BD-AKE282D) and Gal4 activation domain (AD) fusion proteins from plasmids pGAD424-AK (AD-AK) or pGAD424-AK(E282D) (AD-AKE282D) were grown in SD medium supplemented with uracil, adenine, methionine, and histidine (YNB) or in the same medium plus 1 g of l-threonine/liter (YNB+Thr) or 10 μg of FK506/ml (YNB+FK506), and induction of the lacZ reporter gene was quantified by assaying β-galactosidase activity. PJ69-4A cotransformed with vectors pGBT9 (BD) and pGAD424 (AD) was assayed as a control.