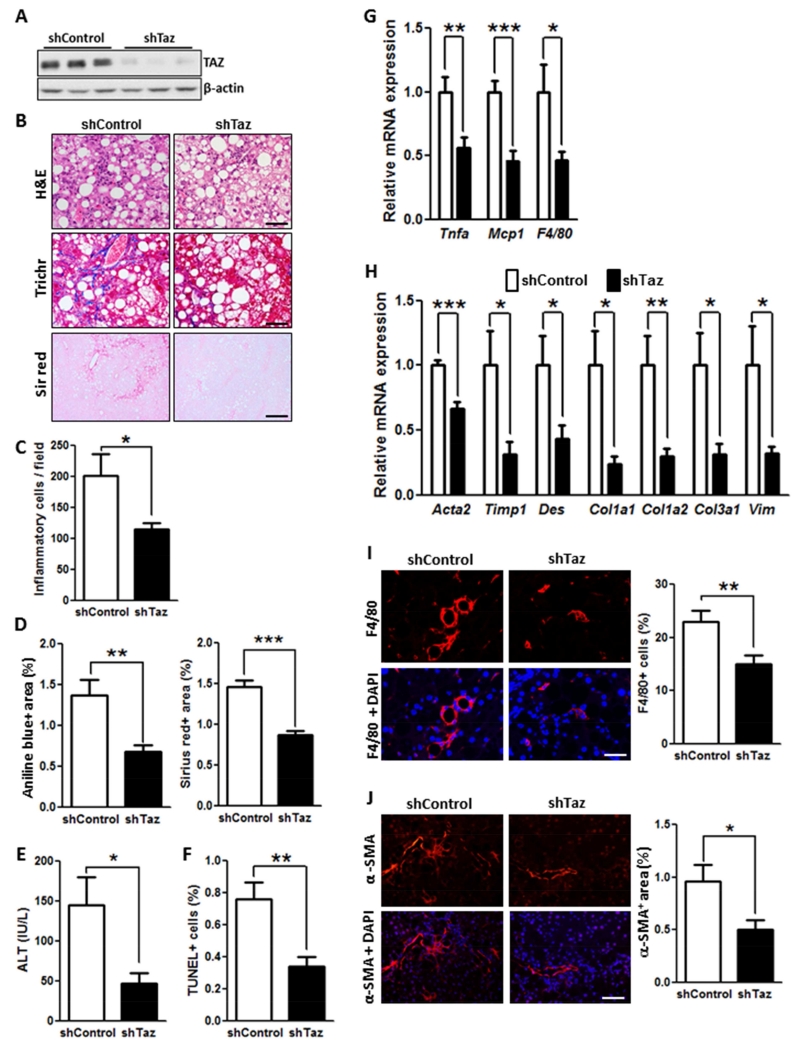
Figure 2. TAZ Silencing Reduces Liver Inflammation, Fibrosis, and Cell Death in FPC-Fed Mice.
The following parameters were measured in male C57BL/6J mice treated with AAV8-H1-shTaz or control vector and then fed the FPC diet for 16 weeks (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.0002, mean ± SEM; n=10 mice/group):
(A) Immunoblot of TAZ in liver, with β-actin as loading control.
(B) Staining of liver sections for H&E (upper panels; Bar, 100 μm), Masson’s trichrome (Trichr) (middle panels; Bar, 100 μm), and Sirius red (Sir red) (lower panels; Bar, 500 μm).
(C) Hepatic inflammatory cells.
(D) Aniline blue- and Sirius red-positive area.
(E) Plasma ALT.
(F) TUNEL+ cells.
(G) mRNA levels of Tnfa, Mcp1, and F4/80 (Adgre1).
(H) mRNA levels of the indicated genes related to fibrosis.
(I) F4/80 immunofluorescence (red) and quantification; DAPI counterstain for nuclei is shown in bottom panels; Bar, 100 μm.
(J) α-SMA immunofluorescence (red) and quantification; DAPI counterstain for nuclei is shown in bottom panels; Bar, 100 μm.