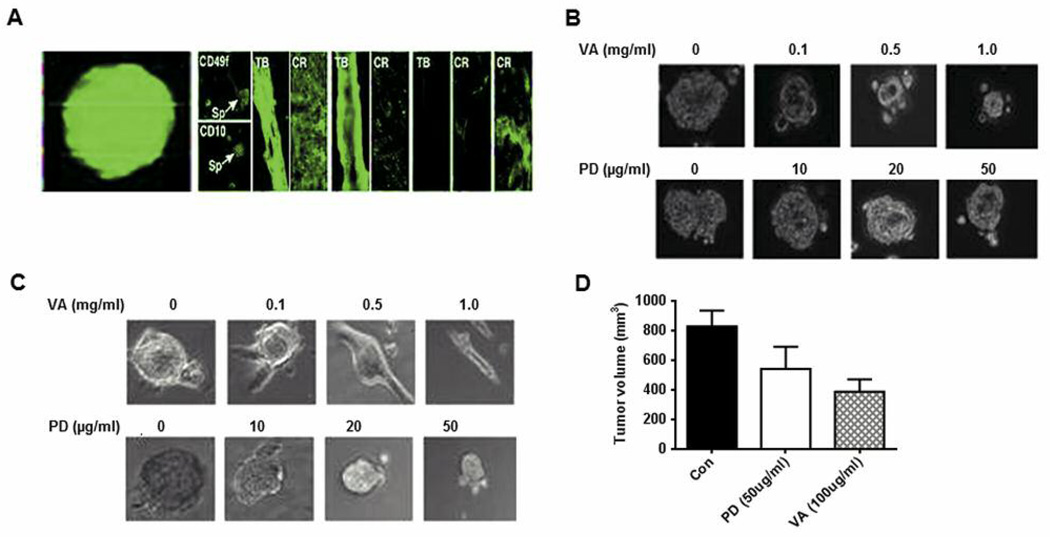
Figure 6.
MCF10A and MCF10AHRAS cells from spheres that can be induced to differentiate into tubular and epithelial-like structures. A: Left panel: 10A and 10AHRAS cells were exposed to suboptimal concentrations of lentivirus expressing eGFP and then grown at clonal dilutions under sphere-forming conditions. After 48 h, micrographs were collected under fluorescence (left) and phase-contrast (right) conditions. Right panel: Spheres were transferred to high-attachment plates and cultured in the presence of serum. After 7 days, the cells were fixed and stained for various differentiation markers. Spheres (Sp), Tubules (TB) and cobblestone-like regions (CR) could be identified. Structures were immunostained for stem-like (CD49f, CD10), myoepithelial (CK 14, SMA) or luminal (CK18, ESA) markers. These structures were analyzed under fluorescence illumination after staining with Alexa Fluor 488 anti-mouse or anti-rabbit FITC conjugated secondary antibody. B: MCF10AHRAS mammospheres treated with VA extracts or PD98059 (PD) at various concentrations for 48 h after which the diameter of the spheres was analyzed under the microscope. C: MCF10AHRAS mammospheres were grown for 6 days after which they were plated on high-attachment plates in the presence of high serum and simultaneously treated with various concentrations of VA extracts or PD. After 48 h of treatment the cells were fixed and analyzed. D: Graphical data of tumor volumes from implanted mammospheres are reported as mean±SD.