Figure 3. Regulation of rDNA transcription by amino acids is mediated through mTORC1 and the downstream target S6K1.
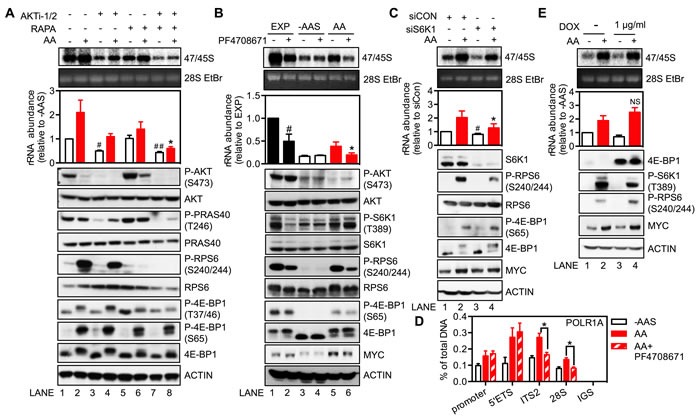
A. and B. HeLa cells were amino acid and serum-starved (-AAS) for 2 hours, pre-treated with either 5 μM AKTi-1/2 or 20 nM rapamycin A. or 10 μM PF4708671 B. for 30 minutes, and then stimulated with all amino acids (AA) for 3 hours. C. HeLa cells were transfected with either non-targeting siRNA control (siCON) or pooled siRNA against S6K1 (siS6K1) for 3 days, and then starved of all amino acids and serum for 2 hours followed by amino acid stimulation for 3 hours. D. HeLa cells were treated as in B. E. HeLa cells stably expressing a doxycycline (DOX)-inducible 4E-BP1-4A mutant plasmid were treated with 1 μg/ml DOX for 24 hours, starved of all amino acids and serum for 2 hours and then stimulated with amino acids for 3 hours. A.-C. and E. In all cases cells were pulse labeled and 47/45S rRNA synthesis analyzed. Representative images and resultant graph (mean +/− SEM) of n = 3-4 experiments. Below the graph are representative immunoblotting images, n = 2-3. D. qChIP analysis to assess the Pol I loading on various regions of the rDNA. n = 3 experiments.A. *p < 0.05 compared to Lane 2; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01 compared to Lane 1. B. *p < 0.05 compared to Lane 5, #p < 0.05 compared to Lane 1. C. *p < 0.05 compared to Lane 2, #p < 0.05 compared to Lane 1. D. NS, not significant compared to Lane 2.
