Figure 2. The existence of individual mitochondria within the intercellular space and junction between pulmonary artery endothelium and smooth muscle cells.
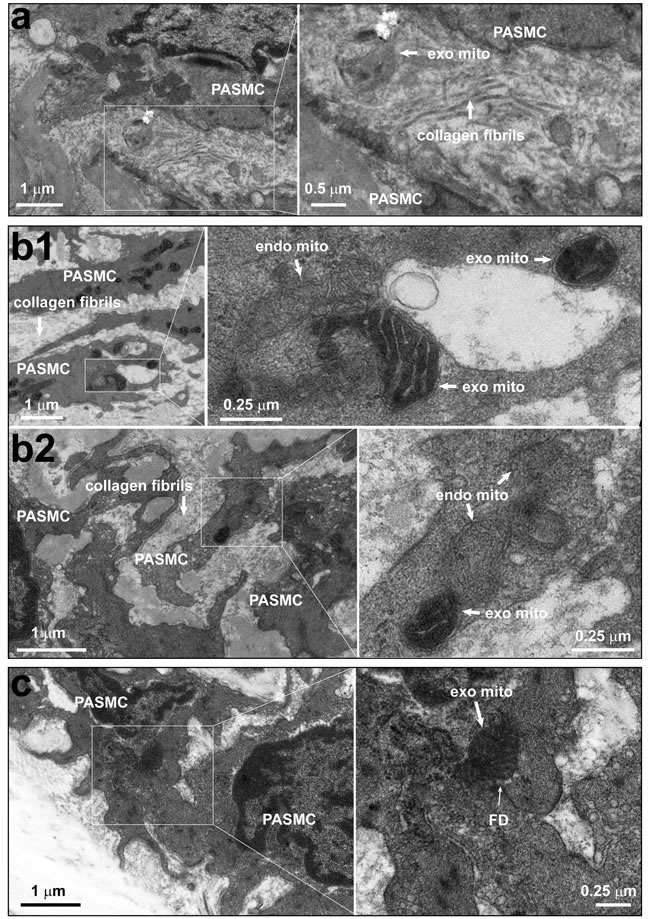
a. Rats were intravenously administrated with mitochondria prepared from Wilson's disease rat liver, which were round with swelling, unclear or disappeared cristae, and then pulmonary arteries were isolated for ultrastructural examination. Representative EM imagings showed one mitochondrion within the intercellular space (a). Out of a total 37 fields with simultaneous existence of endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells from 8 separate pulmonary artery preparations, 9 mitochondria which were round without clear cristae in 7 fields, no mitochondria in the remaining fields were identified within the intercellular space. b.-c. Rats were intravenously administrated with ascorbate peroxidase, APEX-labeled mitochondria prepared from femoral artery smooth muscle cells, then pulmonary arteries were isolated for ultrastructural examination. Representative EM imagings showed the intracellular localization of APEX-labeled, exogenous mitochondria with apparent contrast only in the mitochondrial matrix, not the intermembrane space (b1 and b2); the “on-going” navigation (top right area in the enlarged frame of b1, and b2) and “accomplished” entry (middle area in the enlarged frame of b1) of APEX-labeled, exogenous mitochondria from intercellular space into a smooth muscle cell; and one APEX-labeled, exogenous mitochondrion crossing through a focal discontinuity between endothelial cell and smooth muscle cell (c), the featured myoendothelial junctions allowing bi-directional signaling between endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells in pulmonary arteries. Out of a total of 78 cells examined, 326 and 26 APEX-labeled mitochondria were identified within and crossing into the cytosol, respectively (PAEC, pulmonary artery endothelial cell; PASMC, pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell; FD, focal discontinuity; exo mito, exogenous mitochondria; endo mito, endogenous mitochondria).
