Figure 2. Functional analysis demonstrated that rs5951785 near miR-507 might contribute to the risk of NOA.
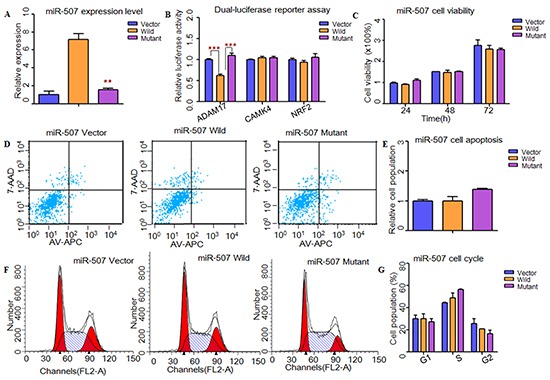
A. RT-PCR was applied to detected mature miR-507 expression levels. The miR-507 expression level was significant down-regulated in mutant type compared with the wild type. B. Dual-luciferase reporter assay was conducted to measure the effects of rs5951785 near miR-507 on promoter-transcriptional activity. It was significantly increased in miR-507 mutant type for ADAM17. C. CCK8 was used to determine the influence of rs5951785 near miR-507 on cell growth. No significant difference was observed in cell proliferation of the rs5951785 near miR-507. D, E. Flow cytometry assay was conducted to measure the effects of rs5951785 near miR-507 on cell apoptosis. (E) Histogram of cell apoptosis was presented to depict cell apoptotic percentages. There was no significant difference of cell apoptosis in rs5951785 near miR-507. F, G. Effects of rs5951785 near miR-507 on cell cycle were analyzed with flow cytometry. (G) Results quantitated in cell cycle were shown in histogram. There was no difference of cell cycle between miR-507 wild and miR-507 mutant type. Each data point represented the mean ± SE from three separate experiments in which treatments were performed in triplicate. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
