Figure 3. CRIB domain and Cdc42-interaction with Mig-6 is indispensable for Mig-6 inhibitory function on EGF-induced migration.
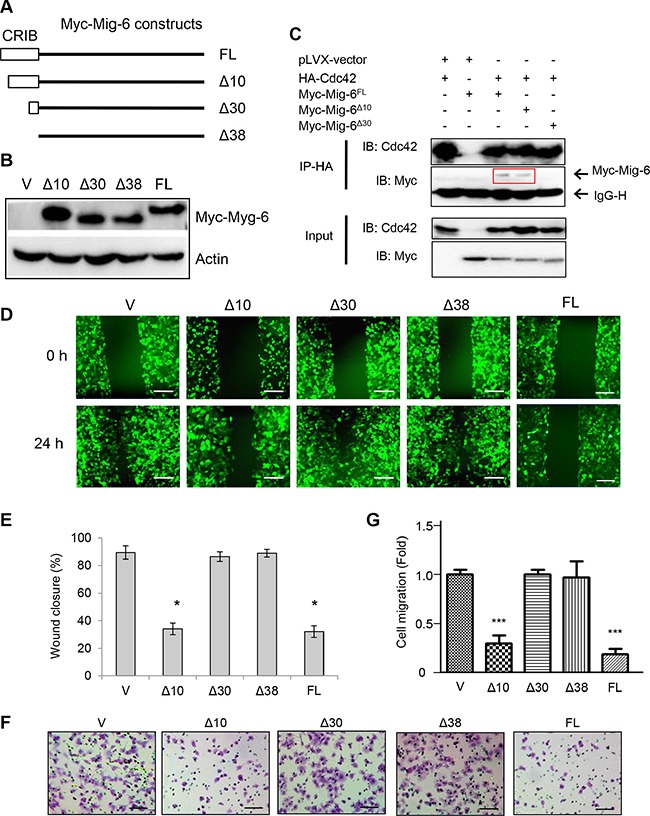
(A) Schematic representation of Mig-6 deletion mutants (not to scale), including full length Mig-6 (FL), Mig-6 lacking the first ten amino acid residues on the N-terminal CRIB domain (Δ10), Mig-6 lacking the first thirty amino acid residues of the CRIB domain (Δ30), and Mig-6 lacking the complete CRIB domain (Δ38). All Mig-6 constructs containing an N-terminal Myc tag were subcloned in to PLVX-GFP lentiviral vector. (B) H1299 cells were stably infected with lentivirus expressing Myc-tagged Mig-6, the deletion mutants, or GFP alone. Cell lysates were subjected to western blotting using antibody for C-Myc, as indicated. (C) cell lysates from 293T cells co-transfected with HA-Cdc42 and Myc-Mig-6 (FL) or a deletion mutant were subjected to IP-western analysis, as shown. Note that Δ30 was unable to interact with Cdc42. (D) Stable H1299 cells were assessed by wound-healing assay in the presence of EGF. Scale bars = 200 μm. (E) Wound-healing assay was quantitated by percentage of wound closure and presented as means and SE. *P < 0.05. (F) Stable H1299 cells were subjected to transwell assays in the presence EGF. Scale bars = 100 μm. (G) Results from three independent transwell assays in duplicate were quantitated and presented as means and SE. ***P < 0.001 (Δ30/Δ38 vs. FL).
