Figure 10. Competitive binding of KU70 by LSD1 and SIRT1.
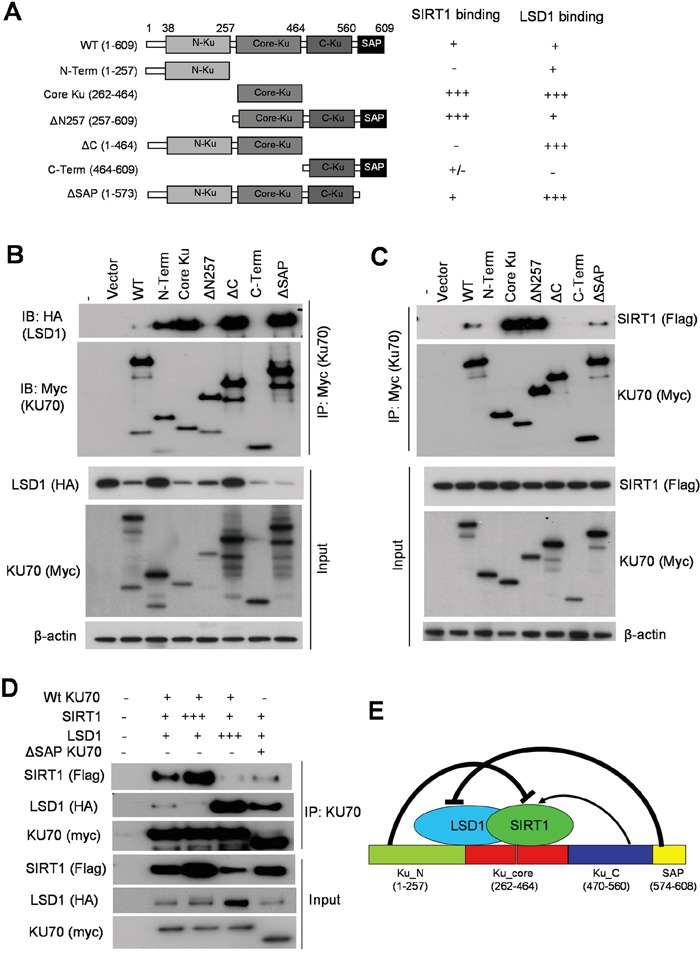
A. Summary of domain mapping of KU70 interaction with LSD1 and SIRT1 in HEK293T cells. Left panel depicts myc-tagged KU70 constructs used along with either wild-type HA-tagged LSD1 (in B) or flag-tagged SIRT1 (in C). Table on the right summarizes relative binding strength for KU70 domains with LSD1 or SIRT1. B, C. Co-IP of myc-KU70 followed by immunoblots of HA-tagged LSD1 (B) or flag-tagged SIRT1 (C) with co-transfected myc-KU70 from HEK293T cells. D. Co-IP of WT or ΔSAP myc-tagged KU70 with varying amounts of WT-SIRT1, WT-LSD1 or vector alone in HEK293T cells. Total amount of transfected DNA was held constant by using empty vector DNA to equalize all samples. E. Schematic summary of KU70 domains for regulating interaction with LSD1 and SIRT1. Both SIRT1 and LSD1 bind to the KU70 core domain. KU70 N-terminus strongly represses SIRT1 binding but C-terminal linker region facilitates SIRT1 interaction. KU70 C-terminal SAP motif strongly represses LSD1 binding.
