Figure 11. The KU70 regulatory domain for SIRT1/LSD1 competition regulated BCR-ABL mutation.
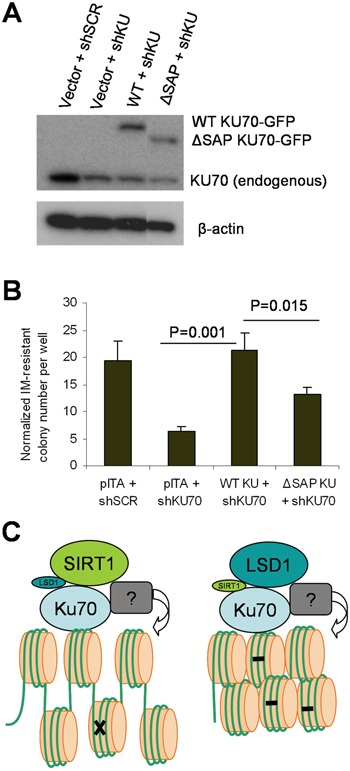
A. Western blot analysis of expression of EGFP-fusion WT or ΔSAP KU70 in KCL-22 cells with knockdown of endogenous KU70 by shRNA targeting 3′ UTR. The ΔSAP KU70 lane was spliced adjacent to the rest of the blot from the same gel. B. The effect of EGFR-fusion constructs on restoring imatinib-resistant BCR-ABL mutant colony formation in KCL-22 cells with KU70 3′ UTR knockdown. C. A schema showing roles of SIRT1 and LSD1 in regulating KU70 for DNA repair. With enhanced SIRT1-KU70 interaction (left), repair is increased with more open chromatin but has more likelihood for acquiring mutation (indicated by x) and developing drug resistance. With enhanced LSD1-KU70 interaction (right), repair is reduced with more “repressive” chromatin resulting in accumulation of DNA damage (indicated by -) and cell lethality. SIRT1 and LSD1 may indirectly modify histones via unidentified factors(indicated by ?) associated with the repair complex.
