Figure 2. Identification of SUMOylation sites in PES1.
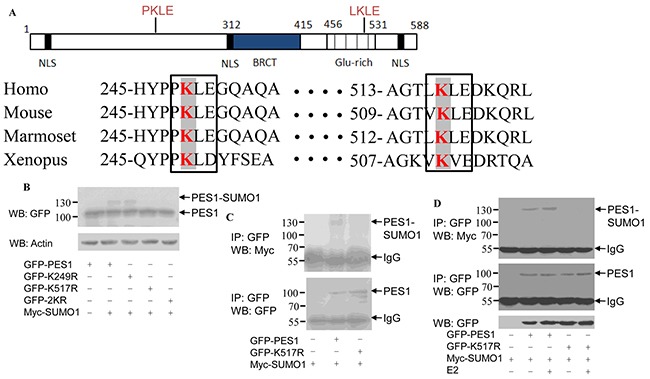
A. Schematic representation of human PES1, showing the conserved lysine residues within the Glu rich region. The amino acids surrounding the two conserved lysine residues were compared with those of PES1 from three other species: mouse, Marmoset and Xenopus. Conserved lysine residues are boxed. B. COS-7 cells were transfected with wild-type GFP-PES1 or its mutants K249R, K517R or K249R/K517R (2KR) and Myc-tagged SUMO-1, and then subjected to western blot with anti-GFP antibody. C. COS-7 cells were transfected with wild-type GFP-PES1 or its mutant K517R as well as Myc-SUMO-1, and then subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-GFP antibody followed by western blot with anti-Myc or anti-GFP antibody. D. MCF-7 cells were transfected with wild-type GFP-PES1 or its mutant K517R as well as Myc-SUMO-1 for 24 h, and the cells were then subjected to serum starvation for 3 days, followed by treatment with 10 nM E2 for 4 h. Cell extract was then prepared and subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-GFP antibody, followed by western blot analysis with anti-Myc or anti-GFP antibody.
