Figure 4.
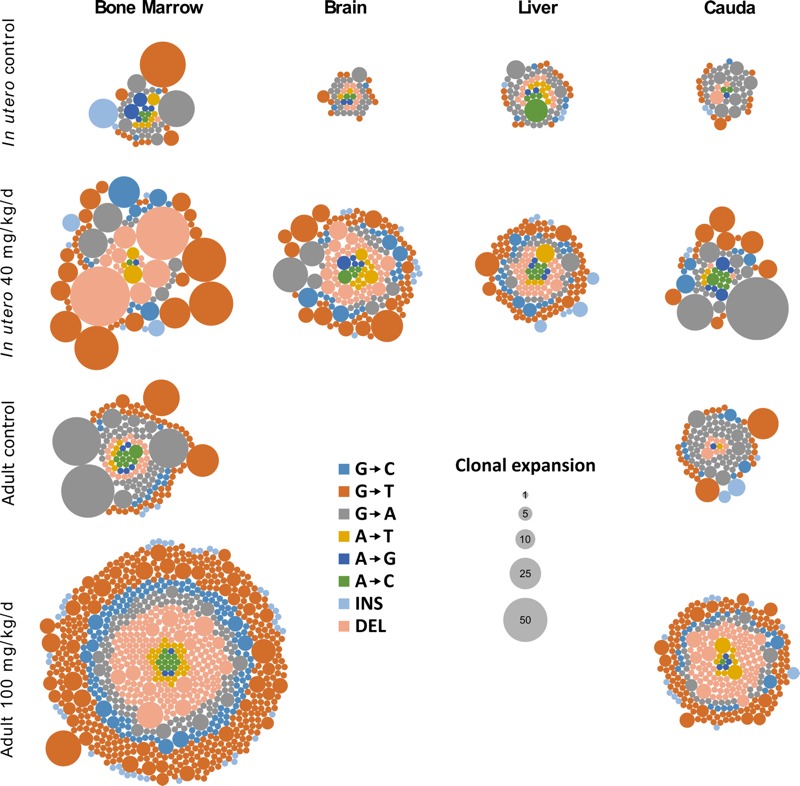
Clonal expansion of the mutations characterized in each somatic tissue and in caudal sperm. The proportion of mutations that underwent clonal expansion is consistently higher in animals exposed to benzo[a]pyrene (BaP) in utero, illustrating the potential for increased mosaicism. As in somatic tissues, the proportion of clonally expanded mutations is higher in BaP-exposed sperm, highlighting the potential for increased germline mosaicism. Compared with exposure in adults (data from Beal et al. 2015 and O’Brien et al. 2016b), in utero exposure results in a higher degree of clonal expansion. Plaques were collected from the 20 mg/kg/day dose group for cadual sperm because of decreased sperm concentration at 40 mg/kg/day. Each circle within a group corresponds to a scored independent mutation, and the area of each circle represents the number of times that mutation was observed per animal. INS, insertion; DEL, deletion.
