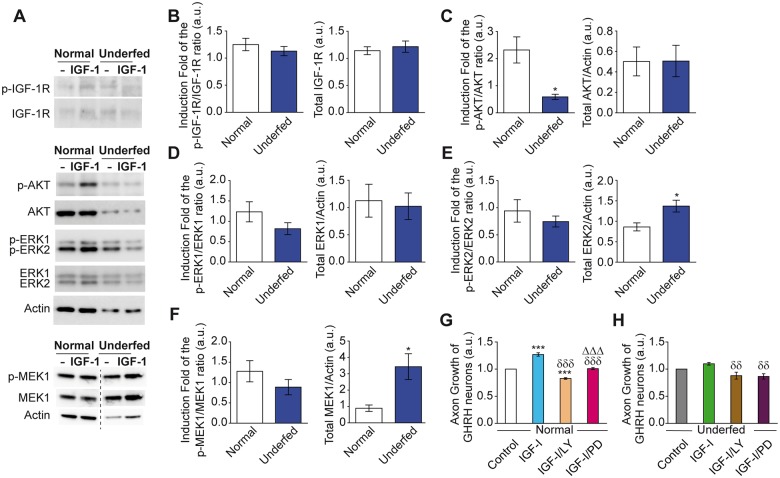
Fig 5. Alterations of the IGF-IR signaling pathways in arcuate explants from underfed pups.
Activation of key elements of IGF-1R signaling pathways were measured by Western blot analysis as illustrated with representative blots in basal condition (-) or 15 min after IGF-I stimulation (IGF-I) (A). Quantification indicates activation of the IGF-1R (fold induction of the p-IGF-1R/ IGF-1R ratio) by IGF-I stimulation relative to basal levels (left panel), and total IGF-1R protein levels (right panel) in arcuate explants harvested from normally fed and underfed pups of both sexes (B). Similarly, activation of AKT (fold induction of the pAKT/AKT ratio) (C), ERK1 (D), ERK2 (E) and MEK-1 (F) are presented (left panels) with their respective total protein levels (right panels) (n = 4–6 per group). In vitro explant cultures indicate that specific inhibition of PI3K by LY294002 (LY) and of MEK by PD0325901 (PD) impaired axon growth of GHRH neurons in normally fed (n = 4 per group) (G) and underfed GHRH-eGFP+ pups (n = 6 per group) (H). All data are presented as the mean ± SEM with Mann Whitney analysis for Western blot analysis with *: p < 0.05 (V-F); and one way-ANOVA analysis with the Newman Keuls post-test (G, H) with *: p < 0.05 and ***: p < 0.001 for each treatment vs. Control; δδ: p < 0.01 and δδδ: p < 0.001 for each treatment vs. IGF-I; Δ Δ Δ: p < 0.001 IGF-I/PD vs. IGF-I/LY.