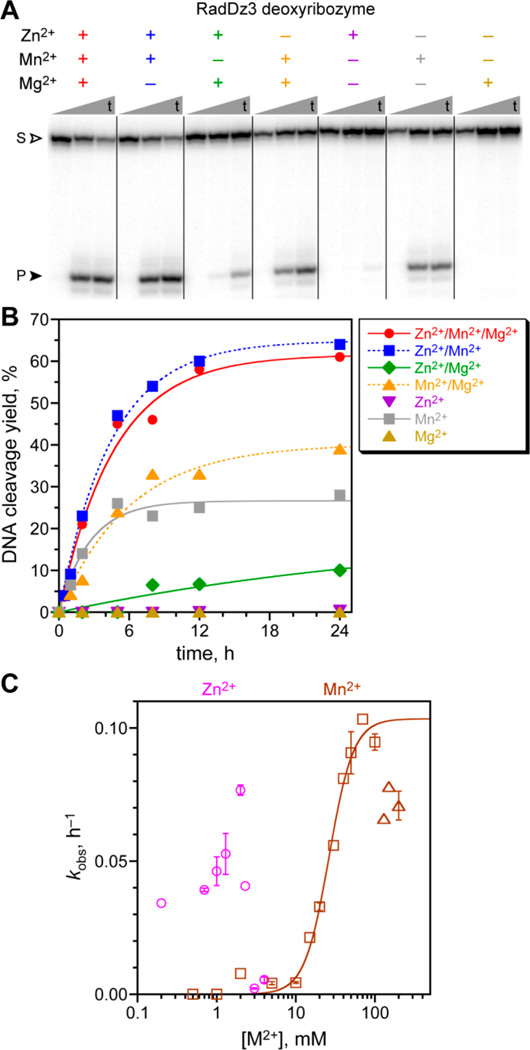
Figure 2.
Assays of the RadDz3 deoxyribozyme that cleaves ssDNA by a radical pathway. Incubation conditions: 70 mM HEPES, pH 7.5, combinations of 1 mM ZnCl2, 20 mM MnCl2, and 40 mM MgCl2 as indicated, and 150 mM NaCl at 37 °C. (A) PAGE analysis of single-turnover DNA cleavage by RadDz3, using 5′-32P-radiolabeled DNA substrate. Representative time points at t = 30 s, 5 h, and 24 h are shown. S = substrate; P = product. (B) Kinetic plots. For this data set, kobs values (h−1): Zn2+/Mn2+/Mg2+ 0.21, Zn2+/Mn2+ 0.22, Zn2+/Mg2+ 0.004, Mn2+/Mg2+ 0.17, Mn2+ 0.38. When Mn2+ was included at 1-300 µM along with 1 mM Zn2+ and 40 mM Mg2+, the DNA cleavage yield was the same as with Zn2+/Mg2+ in the absence of Mn2+ (data not shown), indicating that trace Mn2+ is not responsible for the Zn2+/Mg2+ reactivity. See the Experimental Section for quantitative analysis information on metal ion salts. (C) Determination of metal ion concentration dependence for Zn2+ (in the presence of 20 mM Mn2+) and Mn2+ alone. Data points with error bars were n = 2 (weighted averages; error bars by propagation from curve fit error); data points without error bars were n = 1. For Mn2+ alone, squares were fit, and triangles were not fit. Apparent Kd = 26 ± 2 mM, Hill coefficient n = 2.8 ± 0.4, kmax = 0.10 ± 0.01 h−1.