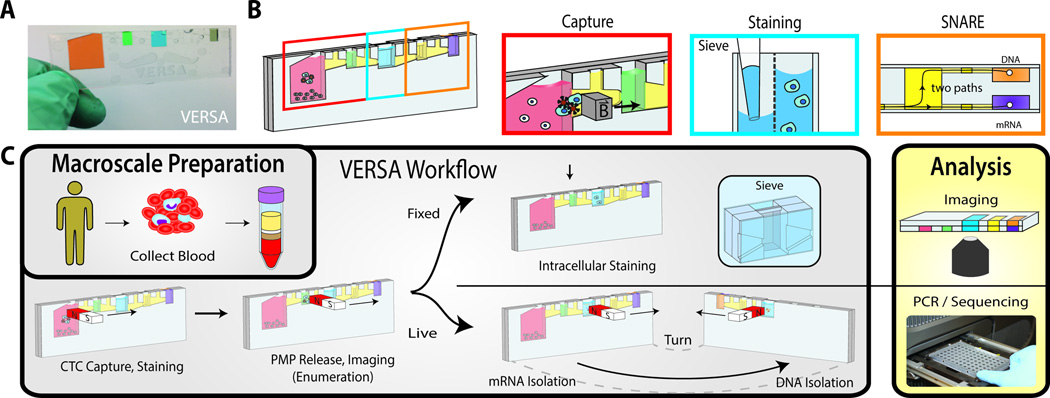
Figure. 1. The VERSA device.
The VERSA integrates efficient cell capture with PMP removal, staining and isolation of mRNA and DNA without dilutive steps. (A) The handheld VERSA is filled with colored dye to differentiate the different chambers. (B) The VERSA is pictured with boxes designating the well used for capture (red), staining (blue) and nucleic acid isolation (orange). (C) A magnet is used to purify PMP-bound CTCs from the input well (pink) through the oil-filled trapezoid into the extracellular staining well (green). After incubation, CTCs are moved into the sieve well (blue), which contains an 8 µm porous membrane, dividing the well into a front and back chamber. The membrane allows low-pressure fluid exchanges to facilitate removal of released and unbound PMPs while preventing cells of interest from passing through. The ability to perform multiple fluid exchanges enables cell permeabilization and incubation with antibodies to intracellular antigens. Cells are imaged in device. mRNA is isolated by lysing cells in device, adding oligo-dT PMPs and moving RNA to the front elution well (orange box, top right). The subsequent addition of silca PMPs with a nuclear lysis buffer enables co-extraction of DNA by magnetic transfer of PMPs to the back well.