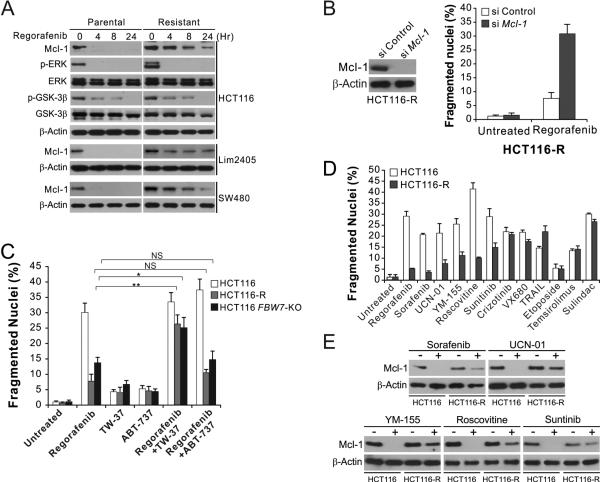
Figure 5. Regorafenib-resistant cells are re-sensitized by Mcl-1 inhibition, and cross-resistant to other anticancer agents that induce Mcl-1 degradation.
(A) Western blotting of indicated proteins in parental and regorafenib-resistant HCT116, Lim2405 and SW480 cells treated with 40 μM regorafenib at indicated time points. p-ERK: Thr202/Tyr204; p-GSK3β: Ser9. (B) HCT116-R cells transfected with control or Mcl-1 siRNA were treated with 40 μM regorafenib for 48 hr. Left, western blot analysis of Mcl-1 knockdown; right, analysis of apoptosis by counting condensed and fragmented nuclei after nuclear staining. (C) HCT116-R cells were treated for 48 hr with 40 μM regorafenib alone or in combination with 1 μM of the Mcl-1 inhibitor TW-37 or the Bcl-2/Bcl-XL inhibitor ABT-737. Apoptosis was analyzed as in (B). (D) Parental and regorafenib-resistant HCT116 cells were treated with 40 μM regorafenib, 20 μM sorafenib, 1 μM UCN-01, 1 μM YM-155, 10 μM roscovitine, 15 μM sunitinib, 10 μM crizotinib, 10 nM TRAIL, 10 μM VX680, 20 μM etoposide, 20 μM temsirolimus, or 120 μM sulindac sulfide for 48 hr. Apoptosis was analyzed as in (B). (E) Western blotting of Mcl-1 in parental and regorafenib-resistant HCT116 cells treated with indicated agents as in (D) for 24 hr. Results in (B)-(D) represent the means ± s.d. of three independent experiments. NS, P>0.05; *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01.