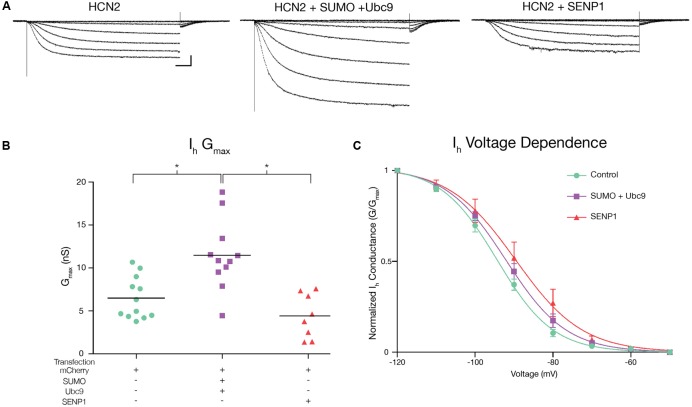
FIGURE 5.
Increased HCN2 channel SUMOylation augments IhGmax. Ih was measured in Hek-HCN2 cells transiently transfected with either mCherry (control), mCherry + SUMO + Ubc9, or mCherry + SENP1. For each treatment group, data were pooled from ≥3 transfections. (A) Representative traces for each treatment group, elicited by stepping the voltage from -50 to -120 mV in 10 mV increments. Scale bars, 500 ms and 200 pA. The kinetics of activation at -120 mV were not altered across treatment groups. Mean activation time constants: control, 400.9 ± 23.01; SUMO + Ubc9, 407.3 ± 33.67; SENP1, 497.4 ± 50.79; one-way ANOVA, F(2,32) = 2.224; p = 0.1246. (B) Plots of Ih Gmax for each treatment group. Each data point represents a single cell. Bar represents the mean. Transfection with SUMO + Ubc9 significantly increased Ih Gmax relative to SENP1 and control treatment groups [asterisks, p < 0.05; One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc, F(2,28) = 13.23; p < 0.0001]. (C) Plots of voltage dependence of activation. Each data point represents the mean ± SEM. There were no significant differences between treatment groups for mean V50 [control, -93.88 ± 1.12; SUMO + Ubc9, -91.6 ± 1.29; SENP1, -87.8 ± 3.03; one-way ANOVA, F(2,32) = 3.006; p = 0.0636] or mean slope [control, -6.61 ± 0.29; SUMO + Ubc9, -7.42 ± 0.41; SENP1, -6.84 ± 0.4; one-way ANOVA, F(2,32) = 1.439; p = 0.252].