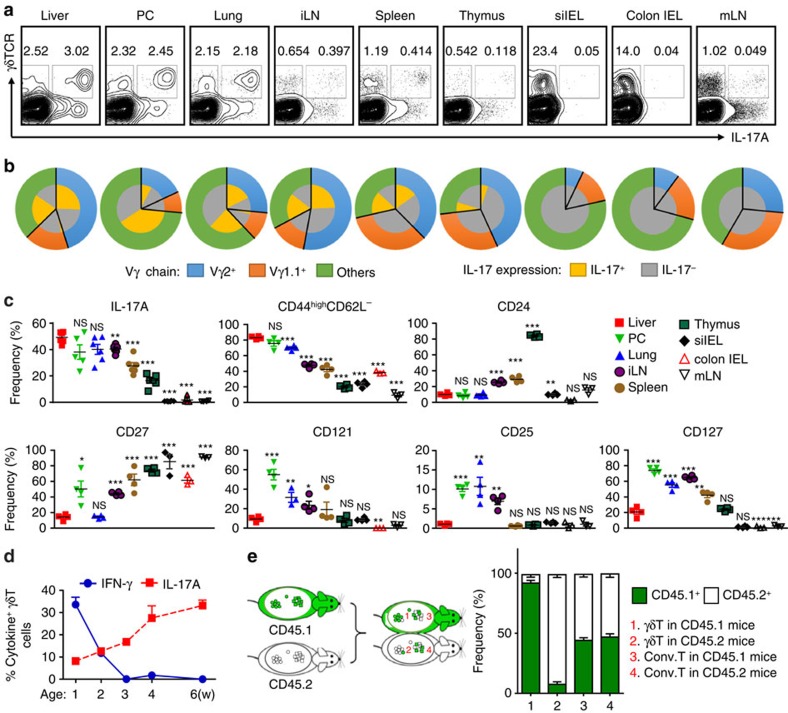
Figure 1. Hepatic γδT-17 cells are major γδT population and liver-resident in adults.
(a) FACS analysis of IL-17A expression by PMA/ionomycin-stimulated γδT cells from the indicated organs of B6 mice, gated on CD3+ T cells. (b) FACS analysis of Vγ chain usage and IL-17A expression by each γδT-cell subtype. (c) Frequency of γδT cells expressing the indicated markers; each dot represents a mouse. (d) IFN-γ and IL-17A expression by hepatic γδT cells at the indicated B6 mouse age over time (n=5/time point). (e) The host origin (CD45.1+ or CD45.2+) of hepatic γδT (CD3+TCRγδ+) and conventional T (CD3+TCRγδ− NK1.1−) cells was identified by FACS analysis in each mouse of CD45.1/CD45.2 parabiotic B6 mouse pairs at 14 days post surgery (n=5 pairs). The data are representative of three independent experiments The mean±s.e.m. is shown. (*P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001. one-way ANOVA with post hoc test). IEL, intraepithelial lymphocyte; iLN, inguinal lymph node; mLN, mesenteric lymph node; PC, peritoneal cavity; si, small intestine.