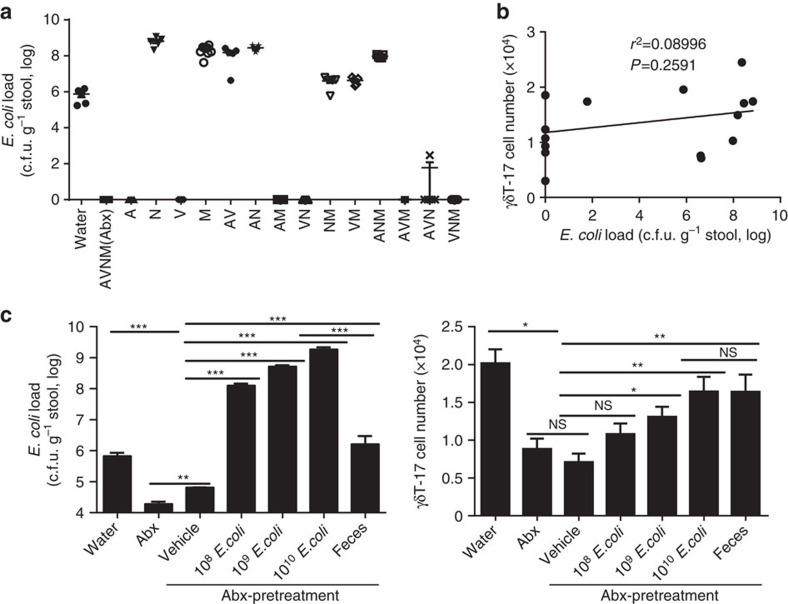
Figure 4. E. coliis sufficient but not essential to promote hepatic γδT-17 cells.
Mice were treated with antibiotics as described in Fig. 3. (a) E. coli in fresh stool were plated and counted on an EMB plate (each dot represents a mouse). (b) The Pearson correlation curve between the γδT-17 cell number and the E. coli load. (c) Abx-pretreated mice continued on Abx (Abx) or untreated (Abx-pretreatment) water, and then the Abx-pretreated mice were intragastrically administered vehicle, 108 c.f.u. E. coli, 109 c.f.u. E. coli, 1010 c.f.u. E. coli or 10 mg fresh faeces (Faeces). E. coli and faeces were from normal mice. The stool E. coli load (3 days post transfer) and hepatic γδT-17 cell numbers (3 weeks post transfer) were detected (n=5, 6, 6, 6, 8, 8, 7; from left to right). The data are representative of three independent experiments. The mean±s.e.m. is shown (*P<0.05; **P<0.01 one-way ANOVA with post hoc test).