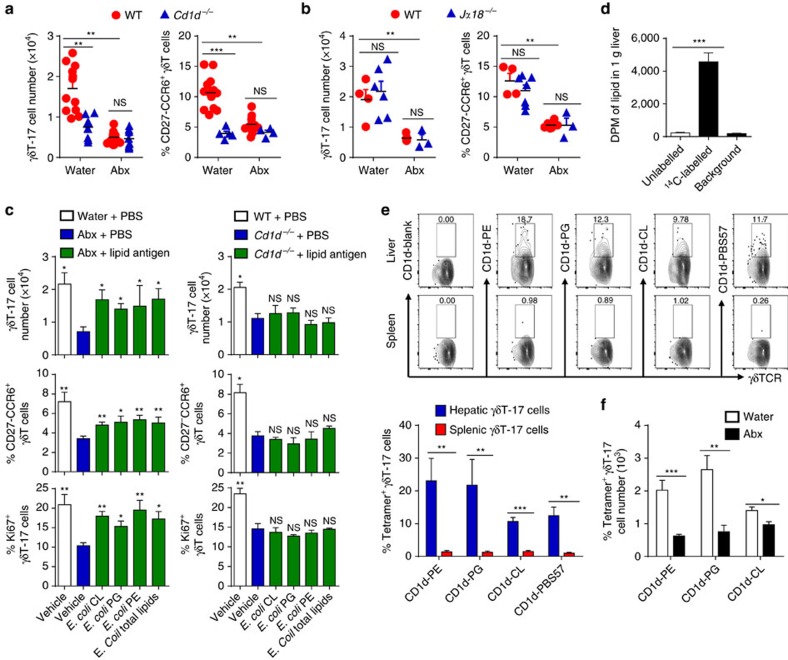
Figure 5. E. colilipid antigens promote hepatic γδT-17 cells in a CD1d-dependent manner.
(a) Age-matched (3 weeks old) and co-housed WT and Cd1d−/− mice were fed water alone (Water) or containing antibiotics (Abx) for 4 weeks, and IL-17A expression and phenotype markers of hepatic γδT cells were evaluated by FACS at 7 weeks old (each dot represents a mouse). (b) WT and Jα18−/− mice were co-housed as in a, and the IL-17A expression and phenotype markers of hepatic γδT cells were then evaluated by FACS (each dot represents a mouse). (c) Abx-treated WT mice or normal water-treated Cd1d−/− mice were i.p. injected with 20 μg E. coli cardiolipin (CL), E. coli phosphatidylglycerol (PG), E. coli phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) or 50 μg total E. coli polar lipid extract six times at 2-day intervals, and IL-17A expression, Ki67 expression and phenotype markers of hepatic γδT cells were evaluated by FACS (n=5 per group). (d) Abx-treated mice were intragastrically administered 1010 c.f.u. of unlabelled or 14C-labelled E. coli, and the radioactivity of the lipids extracted from the liver was evaluated 6 h later (n=3, 4, n/a; from left to right) (e) γδT-17 cells (gated CD45+CD3+TCRγδ+IL-17A+) from the spleens and livers of WT mice were stained with CD1d tetramer loaded with the indicated lipid antigens, and the representative graph and cumulative data are shown (n=4 per group). (f) Mice were treated with antibiotics, and the CD1d-lipid antigen tetramer-specific hepatic γδT-17 cell numbers were evaluated by FACS (n=4 per group). The data are representative of three independent experiments and shown as the mean±s.e.m. (*P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001 one-way ANOVA with post hoc test.).