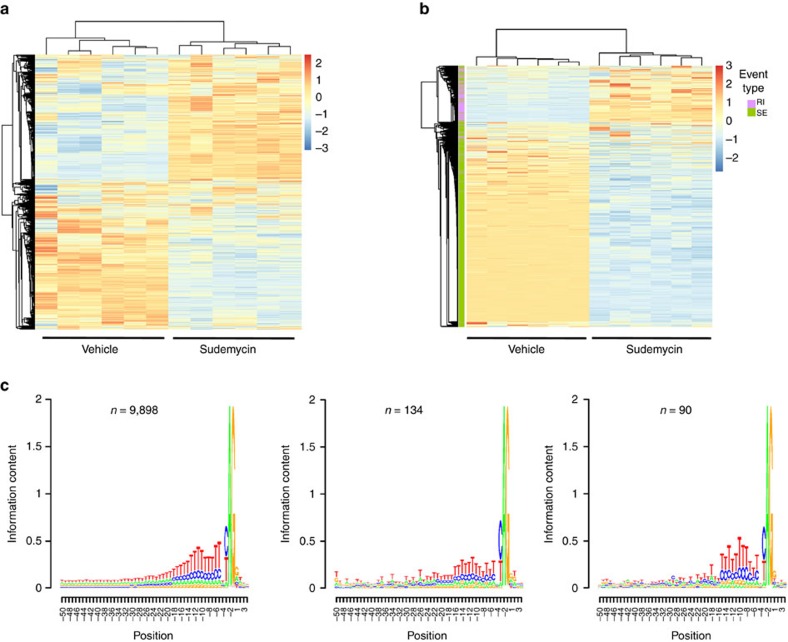
Figure 1. Sudemycin D6 alters gene expression and pre-mRNA splicing in primary human CD34+ haematopoietic cells.
Whole-transcriptome (that is, RNA-seq) analysis was performed on CD34+ cells isolated from human umbilical cord blood following treatment of samples with 1,000 nM Sudemycin D6 or DMSO vehicle for 6 h (n=6). Unsupervised hierarchical clustering of (a) expressed genes and (b) splice junctions. Skipped exons (SE, green) and retained introns (RI, purple) event types are visualized. Values are z-scores computed from regularized logarithm values for genes and from per cent spliced in (PSI or Ψ) values for splicing events. (c) Intronic sequence contexts of cassette exon 3′ splice sites skipped more often in sudemycin- relative to vehicle-treated cells (FDR<5%, |ΔΨ|>10%, left panel) or skipped more often in vehicle-relative to sudemycin-treated cells (FDR<5%, |ΔΨ|>10%, middle panel), along with a context of unperturbed control exons (FDR>50%, |ΔΨ|<0.1%, right panel). Position is relative to the first base in the exon.