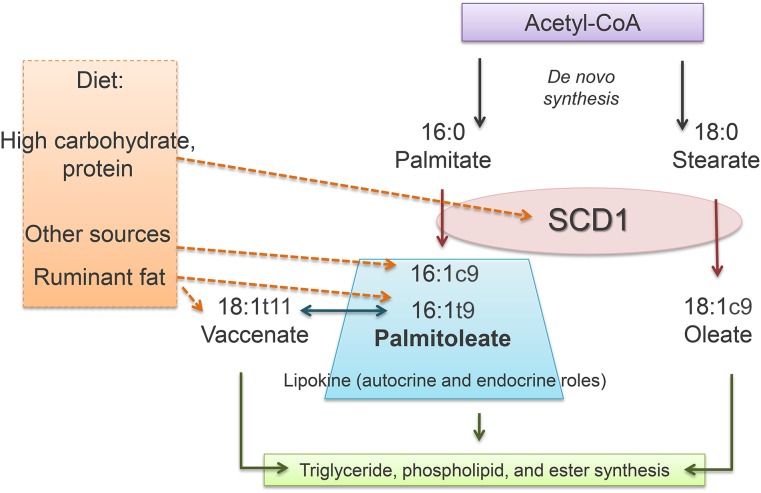
FIGURE 2.
Palmitoleate metabolism. De novo lipogenesis leads to FA synthesis and desaturation via SCD1, with consequent production of 18:1c9 (oleate) and 16:1c9 (cis-palmitoleate). Dietary carbohydrate and protein increase SCD1 activity and the generation of both oleate and cis-palmitoleate. Natural sources of cis-palmitoleate include macadamia nuts and fish oil. Dietary sources of palmitoleate are represented mainly by ruminant fat, which contains 16:1t9 (trans-palmitoleate) and18:1t11 (vaccenate), a precursor of trans-palmitoleate. Palmitoleate, oleate, and vaccenate can be stored in adipose tissue as TGs, cholesteryl esters, or phospholipids. Moreover, palmitoleate is now considered to be a lipokine because of its bioactivity and effects in the liver and muscle. SCD1, stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1.