Figure 7. BMI-1 overexpression protects HCT116 tumor cells against PEITC-induced cytotoxicity and apoptosis.
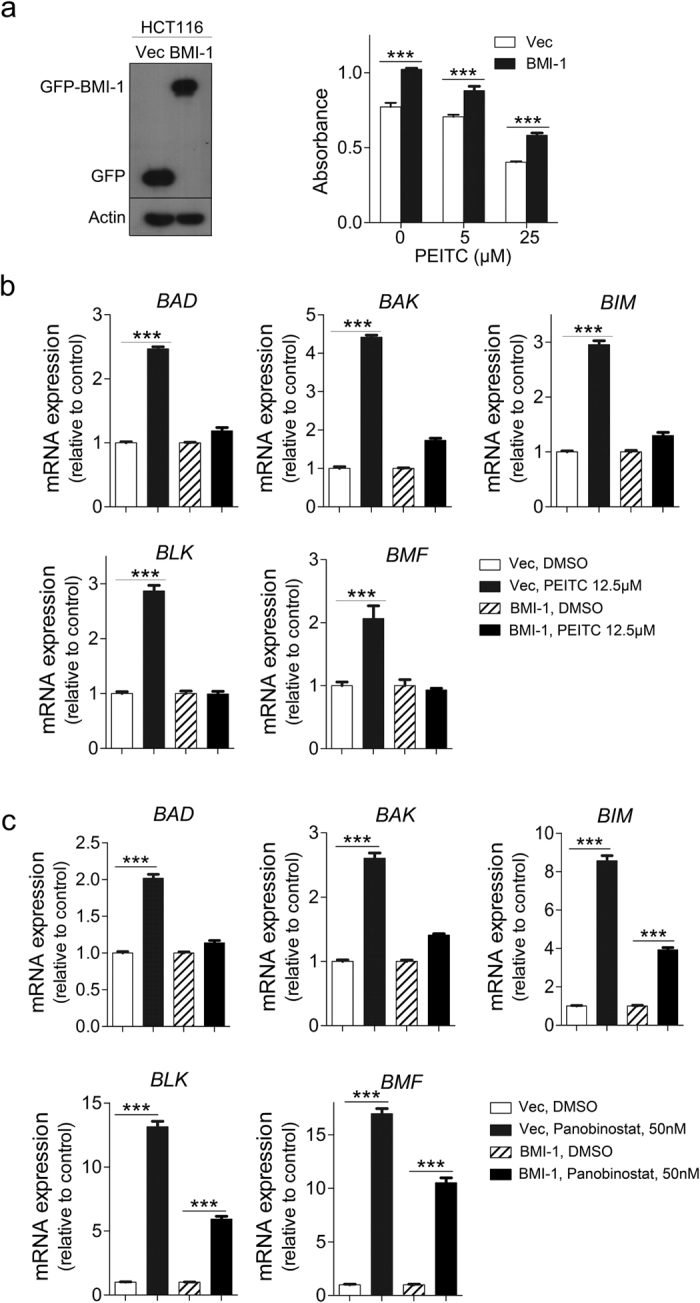
(a) Left panel: Western blot analysis of HCT116 cells expressing GFP only (Vec) or overexpressing BMI-1 (BMI-1). Actin was used as the loading control. Right panel: MTT assay demonstrating that HCT116-BMI-1 cells are partially protected against the cytotoxic effects of PEITC treatment. Error bars represent the mean ± s.d., n = 4. Statistical significance between HCT116-Vec and HCT116-BMI-1 cells was estimated using Student t-test (PEITC 0 μM, p = 0.0001; 5 μM, p = 0.0017; 25 μM, p < 0.0001). (b) Significant upregulation of pro-apoptotic gene expression in HCT116-Vec but not HCT116-BMI-1 cells after 24 h treatment with 12.5 μM PEITC (or DMSO-only control). Error bars represent the mean ± s.d., n = 3. (c) Pro-apoptotic gene expression in HCT116-BMI-1 cells (or HCT116-Vec control) after 24 h treatment with 50 nM panobinostat or DMSO-only vehicle control. Expression levels of pro-apoptotic genes were upregulated by drug treatment in HCT116-Vec cells but not in HCT116-BMI-1 cells, which displayed mRNA expression levels of BAD/BAK comparable to the DMSO-only control and exhibited only limited induction of BIM, BLK, and BMF genes. Error bars represent the mean ± s.d., n = 3. Statistical differences between groups were determined using Student’s t-test (***p < 0.001).
