Figure 1.
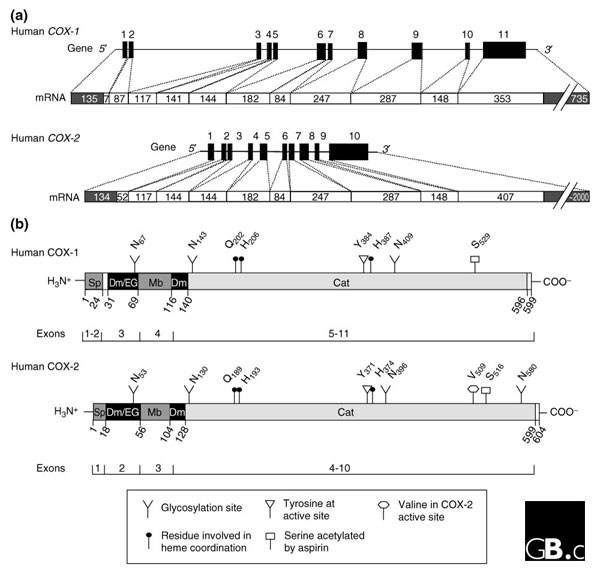
Primary structures of COX genes and COX proteins. (a) Schematic representation of human COX-1 and COX-2 genes and the mRNAs they encode (shown as white bars below the genes). Black boxes in the genes and white boxes in the mRNAs denote exons; numbers above each gene are exon numbers while numbers within the white boxes indicate the size of each exon in nucleotides; single lines in the genes indicate introns and untranslated regions of first and last exons (the latter being shown as gray boxes in the mRNAs). Adapted from [10]. (b) Schematic representation of human COX proteins (all known vertebrate proteins have the same general arrangement). Numbers denote amino-acid residues; the exons encoding each domain are shown on bars below the proteins; important residues are indicated as shown in the key (and with letters in the single-letter amino-acid code, with a subscript number indicating the residue number). Sp, signal peptide; Dm, dimerization domain; EG; epidermal growth factor domain; Mb, membrane-binding domain; Cat, catalytic domain.
